Composition stochiometry
1.When burning 3 g of magnesium, 5 g of magnesium oxide was obtained. Express the composition of this oxide by the mass ratio of the two elements.
Solution:
During the combustion of magnesium, 5–3 = 2 g of oxygen was consumed. The composition of magnesium oxide expressed as the mass ratio of elements is:
m(Mg): m(O) = 3∶2
2.Determine the empirical formula of a compound containing 32.43% sodium, 22.55% sulfur, and 45.02% oxygen.
Solution:
From the percentage composition of the compound, it logically follows that 100 g of the compound contains 32.43 g sodium, 22.55 g sulfur, and 45.02 g oxygen. To determine the ratios of the elements in the compound, we need to know the molar ratios, which are calculated using the molar mass (values taken from the periodic table of elements):
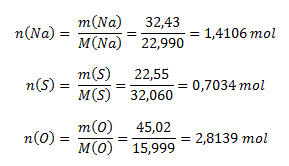
The ratio of molar amounts of the elements in the compound is:
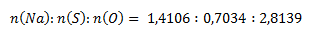
The obtained ratios are adjusted to whole numbers by dividing by the smallest value:
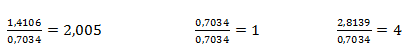
Thus, one mole of sulfur corresponds to 4 moles of oxygen and two moles of sodium. The empirical formula is Na2SO4, sodium sulfate.
3.A compound contains 2.2% hydrogen, 26.6% carbon, and 71.2% oxygen. The relative molecular mass of the compound is 90.034. Determine its molecular formula.
Solution:
As in the second example, we first determine the molar ratios of the elements in the compound.
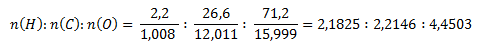
The smallest molar ratio is obtained by dividing by the value for hydrogen:
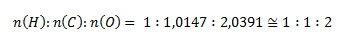
According to this ratio, the stoichiometric formula is HCO2. The relative molecular mass of such a compound would be 45.017, exactly half of the given value. To obtain the given value of 90.034, the elements must be doubled in the molecule. The molecular formula is therefore C2H2O4.
4.Qualitative analysis showed that an organic liquid substance contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Preliminary tests indicated that the substance has no reducing properties and turns universal indicator paper red.
Quantitative analysis determined that the substance contains 39.85% carbon and 6.75% hydrogen. Determine the stoichiometric and molecular formula of the substance.
5.A substance labeled as cobalt(II) sulfate heptahydrate was subjected to thermal analysis. The temperature was chosen so that all the water evaporated. 0.2568 g of the substance was weighed. After decomposition, the residue weighed 0.1471 g. What is the actual formula of the substance?
Please log in to view the solution.
6.The compound contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Its composition is given by the mass ratio of the elements:
7.Determine the molecular formula of a gaseous substance with composition 92.3% carbon and 7.7% hydrogen. One liter of this substance weighs 1.17 g under normal conditions, while one liter of hydrogen under the same conditions weighs 0.09 g.
Please log in to view the solution.
8.Iron reacts with oxygen to form an oxide containing 77.73% iron. Calculate the molar amounts of iron and oxygen in 100 g of the oxide and express their ratio in the smallest whole numbers.
Please log in to view the solution.
9. Determine the stoichiometric and molecular formula of a substance in which the mass ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen is 12 : 1 : 32.
Please log in to view the solution.
10. Chemical analysis showed that a substance contains 1.5% hydrogen, 56.4% arsenic, and 42.1% oxygen. Determine the stoichiometric formula.
Please log in to view the solution.