AC Circuits
1. Characterize alternating electric current and alternating current circuits.
Solution:
Alternating electric current (AC) is a time-varying, periodically changing electric current. Both the magnitude and the direction of the current change. Alternating current is generated based on the law of electromagnetic induction: if a conductor (coil) rotates in a homogeneous magnetic field, an alternating voltage and an alternating current are induced in the conductor.
Alternating current circuits:
1) Circuit with Resistance (Resistor) R
The instantaneous current and voltage are in phase.
Resistive reactance:
2) Circuit with Inductance (Coil) L
The current lags behind the voltage.
Inductive reactance:
3) Circuit with Capacitance (Capacitor) C
The current leads the voltage.
Capacitive reactance:
4) RLC, RL, RC, LC Circuits in Series
Impedance:
RLC:
RL:
RC:
LC:
Condition: At resonance,
2.An alternating voltage with frequency f = 50 Hz has amplitude Um = 200 V. Write the equation for the alternating voltage. Find the instantaneous value of the voltage at time t = 4 ms.
Solution:
Analysis:
Um = 200 V, f = 50 Hz, t = 4 ms, u = ?
u = Um·sin(ωt)
u = Um·sin(2·π·f·t)
u = 200 V·sin(2·π·50·t)
u = 200·sin(100·π·t)
u = 200 V·sin(100·π·50·s-1·4·10-3s) = 200 V·sin(72°)
u = 200 V·0.951 = 190.2 V
u = 190.2 V
The equation of the alternating voltage is u = 200·sin(100·π·t).
The instantaneous value of the voltage at time t = 4 ms is u = 190.2 V.
3.The alternating current in an electrical circuit is described by the equation i = 5·sin(200·π·t) [A]. Determine the current amplitude, the frequency and the period of the current. Also determine the instantaneous value of the current at time t = 1.25·10–3 s.
Solution:
i = 5·sin(200·π·t) [A]
i = Im·sin(ω·t)
Im = 5 A,
ω·t = 200·π·t, 2·π·f = 200·π, 2·f = 200 s-1, f = 100 Hz 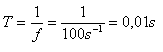
i = 5·sin(200·π·t) [A]
i = 5·sin(200·π·1.25·10-3 s) [A]
i = 5·sin(45°) = 5·0.707 A = 3.54 A
i = 3.54 A
Im = 5 A, f = 100 Hz, T = 0.01 s, i = 3.54 A.
4.Determine the reactance of a coil with inductance 500 mH in an AC circuit with frequency 50 Hz. Calculate the current amplitude if the voltage amplitude is 314 V.
Please log in to view the solution.
5. Determine the reactance of a capacitor with capacitance 20 μF in an AC circuit with frequency 50 Hz. Also calculate the voltage amplitude if the current amplitude is 2 A.
Please log in to view the solution.
6.An inductor with inductance 2 H and winding resistance 20 Ω is first connected to a DC voltage source of 20 V and then to an AC voltage source with the same RMS value and frequency 50 Hz. Determine the current in the circuit in both cases.
Please log in to view the solution.
7. An AC circuit with RMS voltage 200 V and frequency 50 Hz is connected to a series circuit formed by a capacitor with capacitance 16 μF and a resistor with resistance 150 Ω. Determine the impedance of the circuit, the current in the circuit, and the voltages across the capacitor and the resistor.
Please log in to view the solution.8.An oscillatory circuit consists of a coil with inductance 0.1 mH and a capacitor with capacitance 100 pF. Determine the resonance frequency.
Please log in to view the solution.
9.A coil with L = 5·10–2 H, whose winding has resistance R = 10 Ω, is connected in series with a capacitor C = 2·10–6 F. An alternating current with amplitude Im = 0.1 A and f = 500 Hz flows through the circuit. Determine the impedance Z of the circuit and the voltage amplitude Um.
Please log in to view the solution.
10. A series AC circuit consists of a resistor with R = 90 Ω, a coil with inductance L = 1.3 H, and a capacitor with capacitance C = 10–5 F. The circuit is connected to an AC voltage source with amplitude Um = 100 V and frequency f = 50 Hz. Write the equations for the instantaneous values of voltage and current in the circuit.
Please log in to view the solution.
11.An alternating current has an amplitude of 100 mA and a frequency of 2 MHz. After what time from the initial moment (i = 0) will the instantaneous value of the current be 25 mA?
Please log in to view the solution.12.A coil with negligibly small resistance is connected to an AC circuit with frequency 50 Hz. With a voltage of 24 V, a current of 0.5 A flows through the coil. Determine the inductance of the coil.
Please log in to view the solution.13.A capacitor is connected to an AC circuit with voltage Umax = 220 V and frequency f = 50 Hz. A current Imax = 2.5 A flows through the circuit. Determine the capacitance of the capacitor.
Please log in to view the solution.
14.A capacitor with capacitance C = 2 μF is connected to an AC circuit with frequency f = 500 Hz. Another capacitor with the same capacitance is connected in parallel to the first one. How must the current frequency be changed so that the circuit capacitance does not change?
Please log in to view the solution.15.A capacitor with capacitance C = 16·10–6 F is connected to a source of AC voltage Um = 24 V with period T = 2·10–3 s. Determine Imax in the circuit.
Please log in to view the solution.16.A capacitor is connected in series with a light bulb. The circuit is connected to a voltage of 220 V at 50 Hz. What capacitance must the capacitor have so that the bulb’s rated voltage and current are 55 V and 0.5 A?
Please log in to view the solution.17.A choke with inductance 2 H and winding resistance 20 Ω is first connected to a DC voltage source of 20 V and then to an AC voltage source with the same value and frequency 50 Hz. Determine the current in both cases.
Please log in to view the solution.18.To a choke with inductance 60 mH and resistance 10 Ω we want to connect a resistor “x” in series so that the resulting circuit has impedance 26 Ω. The AC frequency is 50 Hz.
Determine the resistance of resistor “x”.
19.In a series RLC circuit, it holds that at frequency 50 Hz, XL = 2·XC. How must the frequency change so that resonance occurs?
Please log in to view the solution.20.In an AC circuit with voltage 230 V and frequency 50 Hz, a resistor (R = 200 Ω), a coil (L = 1 H), and a capacitor (C = 5·10-6 F) are connected in series.
- What current flows through the circuit?
- What is the phase difference between voltage and current?
21.Show by calculation (use the formula sin(α – β) = sinα·cosβ – cosα·sinβ) that for a three-phase electric current it holds that u1 + u2 + u3 = 0.
Please log in to view the solution.