Astrophysics
1.How are distances, masses, and brightness of stars determined in astrophysics?
Solution:

2.How is information about stars and the universe obtained?
Characterize:
- Wien’s displacement law
- Stefan–Boltzmann law
- Radiant flux
- Radiant power
- Characteristics of the Sun
- Expansion of the universe
- Doppler’s law
- Hubble’s law
Solution:

Hubble’s law:
3.Calculate how long it takes light in vacuum to travel a distance equal to
- a) the diameter of the Solar System (s = 80 AU)
- b) the diameter of the Galaxy (s = 30 kpc)
Solution:
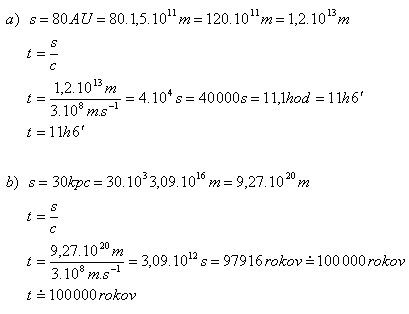
Light travels the diameter of the Solar System in 11 hours, the diameter of the Galaxy in about 100,000 years.
4.Calculate the average density of matter in the Solar System. Assume all the mass of the system is in the Sun (Mo = 2·1030kg) and that the Solar System is a sphere with radius R = 40 AU.
Please log in to view the solution.5.The Sun orbits the center of the Galaxy at v = 250 km·s-1, approximately in a circle with radius r=10 kpc. Determine the orbital period of the Sun. What gravitational force attracts the Sun to the center of the Galaxy?
Please log in to view the solution.6.Consider a globular cluster with mass MGC = 2·105Mo orbiting the center of the Galaxy (MG=1.4·1011Mo) in a circle of radius r=12 kpc. Determine:
- a) the force with which the cluster is attracted to the center of the Galaxy
- b) the centripetal acceleration of the cluster
- c) the velocity of the cluster relative to the center of the Galaxy
7.Derive the formula for calculating the mass of a star (planet) using its satellite.
Please log in to view the solution.8.Calculate the mass of the planet Mars using its moon Deimos, which orbits Mars in a circle of radius r = 23.5·106m, with an orbital period of 1.26 Earth days.
Please log in to view the solution.9.Jupiter’s moon Europa orbits Jupiter in a circle with radius r1 = 6.71·108m and orbital period T = 3.88 days. Calculate how many times the mass of Jupiter is greater than the mass of Earth.
Please log in to view the solution.10.The total mass of a binary star is 3.5Mo, the components orbit their common center of mass with period T = 320 years. Determine the mutual position of the components perpendicular to the line of sight, which we would see under an angle π = 3.1″ and the distance of the binary star from the Sun.
Please log in to view the solution.11.The apparent stellar magnitude of the Sun is -26.8m. Calculate its absolute magnitude M.
Please log in to view the solution.12.To what distance can we use a supernova to measure galaxy distances if its maximum absolute magnitude is –16M and we have a telescope observing stars up to apparent magnitude +22m?
Please log in to view the solution.13.What parallax π does a star have if the difference between its apparent and absolute magnitudes is +8?
Please log in to view the solution.14.What is the wavelength at which maximum radiation occurs and the intensity of radiation of a star with temperature 30,000K?
Please log in to view the solution.15.A red giant has surface temperature 3500K, radius R = 36Ro, mass M = 3.6Mo. Calculate its average density ρ and radiant power L. (σ = 5.67·10-8W·m-2·K–4)
Please log in to view the solution.16.Calculate the radius and average density of a white dwarf with mass M = 2.35Mo, surface temperature T = 12,500K, radiant power L = 0.0036Lo. Ro = 6.96·108m, T0 = 5780K
Please log in to view the solution.17.What radiant flux from the Sun falls on an area of S = 1m2 (Radiant power of the Sun L=3.83·1026W)
- on Venus (r = 0.72AU)
- on Jupiter (r = 5.2AU)
18.A star has apparent magnitude m1=4. What would be its apparent magnitude m2 if it were at twice the distance?
Please log in to view the solution.19.Consider a distant galaxy that is moving away from our Galaxy with a velocity v = 6000 km·s-1. What wavelength of the hydrogen spectral line will we measure if its original wavelength is 656.3 nm? At what distance from us is this galaxy likely located?
Please log in to view the solution.20.Determine the time over which our universe has been expanding. Determine the time that has elapsed from the “Big Bang” to the present.
Please log in to view the solution.