Kinetics
1. You go on vacation by car on the highway for 3 hours at a speed of 110 km·h-1. Then you stop for 30 minutes. You continue with a two-hour drive at a constant speed of 90 km·h-1 to the destination. Determine the average travel speed.
Solution:
Analysis:
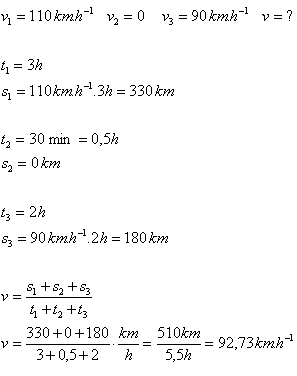
The average travel speed was v = 92.73 km·h-1.
2.The highway section is 25 km long. The maximum allowed speed is 110 km·h-1. The driver covered this section in 12 minutes. Did they exceed the maximum allowed speed on the highway?
Solution:
Analysis:
s = 25 km = 2500 m; t = 12 min = 720 s.
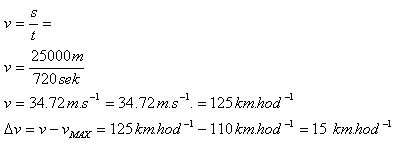
The driver exceeded the allowed speed by 15 km·h-1.
3.A convoy of military vehicles is 2 km long. It moves at a constant speed of 30 km·h-1. The distance from the front of the convoy to the last vehicle was covered by a courier at an average speed of 50 km·h-1. Back, at a speed of 60 km·h-1. How much time did the courier need and what distance did they cover?
Solution:
Analysis:
In the opposite direction of the convoy:
In the same direction as the convoy:
Total time:
Total distance:
4. A freely falling body has a speed of 3.0 m·s-1 at point A and a speed of 7.0 m·s-1 at a lower point B. Determine the time to cover distance AB. What is the distance between points A and B? With what speed will the body hit the ground if its motion from point B to the ground lasts another 2 s?
Please log in to view the solution.
5.A swimmer whose speed relative to the water is 0.85 m·s-1 swims in a river where the water flows at 0.40 m·s-1. Determine the time to swim from point A to B, which are 90 m apart, if the swimmer swims:
- a) downstream
- b) upstream
- c) perpendicular to the current (the resultant speed is perpendicular to the current speed).
Please log in to view the solution.
6. A motorboat traveling on a river covered a distance of 120 m when going downstream in 14 s, and when going upstream in 24 s. Determine the boat’s speed v1 relative to the water and the river current speed v2.
Please log in to view the solution.
7.A motorist covered the first third of the distance at a constant speed v1, and the remaining two thirds at v2 = 72 km·h-1. The average speed v was 36 km·h-1. Calculate v1!
Please log in to view the solution.
8.A car traveling at 90 km·h-1 saw a stationary truck 60 m ahead. The driver braked and achieved a deceleration a = 5 m·s-2. What was the car’s braking distance? Did it hit the obstacle?
Please log in to view the solution.
9.A rocket reaches the second cosmic speed of 11 km·s-1 after traveling a distance of 200 km. How long does it take to achieve this? What is its acceleration?
Please log in to view the solution.
10.A cart on the rails of a demonstration set moves with constant acceleration a = 0.08 m·s-2 (v0 = 0, s0 = 0)
- Calculate the distances the cart travels at times t = 1 s, 2 s, 3 s, 4 s, 5 s.
- Determine the distances traveled in each consecutive second. In what ratio are these distances?
Please log in to view the solution.
11.The engineer of an express train, which was moving at v1 = 108 km·h-1, saw a freight train 180 m ahead moving in the same direction at v2 = 32.4 km·h-1. The engineer began braking and the train decelerated at a = 1.2 m·s-2. Determine whether the trains will collide.
Please log in to view the solution.
12.The second hand of a clock is one third longer than the minute hand. In what ratio are the speeds of their tips?
Please log in to view the solution.
13.The Earth orbits the Sun in approximately uniform circular motion in 365.25 days. What is the speed of the Earth if the Earth–Sun distance is approximately 150 million kilometers?
Please log in to view the solution.
14.The speed of uniform circular motion of a satellite around the Earth is 7.46 km·s-1. The satellite moves at an altitude of 800 km above the Earth’s surface. (R = 6378 km) Determine the orbital period T of the satellite around the Earth.
Please log in to view the solution.
15.What is the minimum speed a motorcyclist must have to ride in all directions on the inner surface of a hollow sphere with radius R = 6 m? The center of mass of the motorcycle and rider is 0.9 m from the surface.
Please log in to view the solution.
16. A carousel seat is attached at a distance of 240 cm from the center of rotation and makes 18 revolutions per minute. Determine its tangential speed and centripetal acceleration.
Please log in to view the solution.