Lenses
1. Explain the formation of an image with lenses.
Solution:
A lens is a homogeneous body bounded by:
-
two spherical surfaces
-
a spherical surface and a plane
A lens forms an image by refraction of light. There are two types of lenses:
-
converging (convex)
-
diverging (concave)
Thin lens with equal radii of curvature:
-
f = focal length
-
r = 2·f = radius of curvature
-
a = object distance
-
á = image distance
-
y = object height
-
ý = image height
Magnification of the image:
Object space = space in front of the lens (left side)
Image space = space behind the lens (right side)
Sign convention:
-
r₁, r₂ positive (negative) – spherical surfaces convex (concave)
-
a positive – object in the object space
-
á positive (negative) – image in the image (object) space
-
y, ý positive (negative) – above (below) the optical axis
Lens equation:
n₂ = refractive index of the lens, n₁ = refractive index of the surrounding medium
Optical power of a lens Φ:
-
Φ > 0 → converging lens
-
Φ < 0 → diverging lens
2. Determine the focal length of the lenses if their optical power is:
- a) φ = 2D
- b) φ = -12D
Solution:
Analysis:
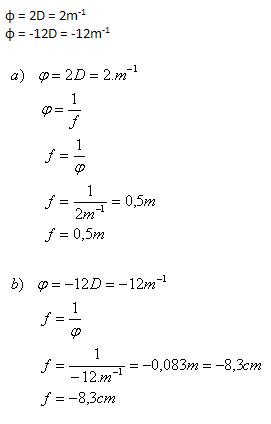
The focal length of the lenses is 0.5m and –8.3cm.
3. Determine the optical power of a biconvex lens with r1 = r2 = 0.4m made of rock salt (n2 = 1.537) in air (n1 = 1) and in carbon disulfide (n1 = 1.609).
Solution:
Analysis:
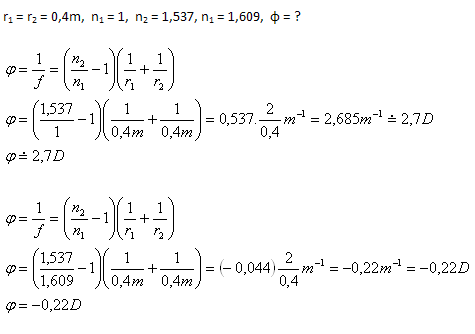
The optical power of the lens in air is 2.7D, in carbon disulfide –0.22D.
4. At what distance from the objective (convex lens) should the projection screen be placed so that the image is magnified 50 times? The focal length of the lens is f = 10cm. For a real image formed by a convex lens, Z < 0.
Please log in to view the solution.
5. The distance between a candle and a wall is 100cm. At what distance from the candle (between the candle and the wall) should a convex lens with f = 9cm be placed so that a sharp image forms on the wall?
Please log in to view the solution.
6. In front of a convex lens, a candle with a flame height of 5cm is placed. The lens created an image on the screen with a flame height of 15cm. When the candle was moved 1.5cm farther from the lens, a sharp image appeared again on the screen with a height of 10cm. Determine the focal length of the lens.
Please log in to view the solution.
7. A thin glass lens has in air (n = 1) a refractive index n1 = 1.7 and an optical power φ = 4D. What optical power will the same lens have when immersed in a liquid with refractive index n2 = 1.85?
Please log in to view the solution.
8. A cylindrical beam of rays parallel to the optical axis falls on a concave lens. The beam diameter is 5cm. On a screen placed 20cm behind the concave lens, a circular spot with a diameter of 15cm is formed. Determine the focal length of the concave lens.
Please log in to view the solution.
9. A thin concave lens has a focal length of 20cm. A candle is placed in front of the lens first at 20cm, then at 30cm. Calculate the distance between the images of the candle flame formed by the lens (f < 0).
Please log in to view the solution.
10. A meniscus lens with a refractive index of 1.6 has an optical power of φ = 1.25m-1. One of the lens surfaces has a curvature radius of 120mm. Determine the curvature radius of the other surface.
Please log in to view the solution.
11.Isaac Newton in his work *Optics* (1704) published the lens equation in the form f2 = ( a – f ).( a/ - f ). Show that it is identical to the equation used at present.
Please log in to view the solution.12.We look through a diverging lens with a focal length of 10 cm at an object located 30 cm from the lens. Where and what kind of image will we see?
Please log in to view the solution.13.At what distance from a diverging lens with φ = -5D must an object be placed in order to obtain an image reduced four times.
Please log in to view the solution.14.The object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a converging lens with fS = 20 cm. How does the image size change if we replace the converging lens with a diverging lens with fR = –20 cm?
15.The distance of the object from a diverging lens is 5 times greater than its focal length. Determine the properties of the image.
Please log in to view the solution.16.A meniscus lens made of glass (n2 = 1,5) has a focal length of 24 cm. What are the radii of curvature of both optical surfaces if the concave surface has twice the radius of curvature of the convex one?
Please log in to view the solution.17.A glass converging lens has a focal length f1 = 20 cm in air. What is the focal length f2 of the lens in water?
Please log in to view the solution.18.A plano-convex lens whose spherical surface has a radius of 15 cm forms a real image magnified 9 times. What are the distances of the object and the image from the lens, if nS = 1.5?
Please log in to view the solution.19.Determine the focal length of a system consisting of two touching thin lenses with focal lengths 10 cm and 40 cm, if:
- a.) both lenses are converging lenses
- b.) the first lens is converging, the second diverging.
20.Explain Bessel’s method for determining the focal length of a converging lens. F.W. Bessel (1787–1846) was a German physicist.
Please log in to view the solution.