Rigid body
1.What do we know about the properties of a rigid body?
Solution:
rigid body is an ideal body whose shape and volume do not change under the action of external forces. External forces cause a change in the state of motion of the rigid body. The motion of the body can be:
a.) Translational
b.) Rotational motion of a rigid body around an axis is a motion in which every point of the body has the same angular velocity at a given time.
The rotational effect of a force on a rigid body is expressed by the moment of force:
F is the acting force, is the lever arm. The lever arm is the distance of the force vector line from the axis of rotation of the body.
Moment theorem: The rotational effect of forces acting on a rigid body cancels out if:
Moment of inertia is a measure of a body's resistance to rotational motion:
Kinetic energy of a rotating body:
2.At the corners of a rectangular plate with sides a = 30 cm, b = 40 cm act forces F1 = 10 N, F2 = 20 N, F3 = 30 N, F4 = 40 N. The plate can rotate about an axis perpendicular to the plate passing through vertex A. What is the resultant moment of the forces acting on the plate?
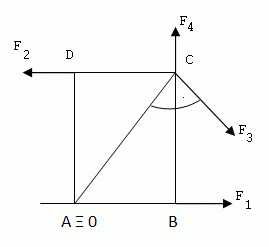
Solution:
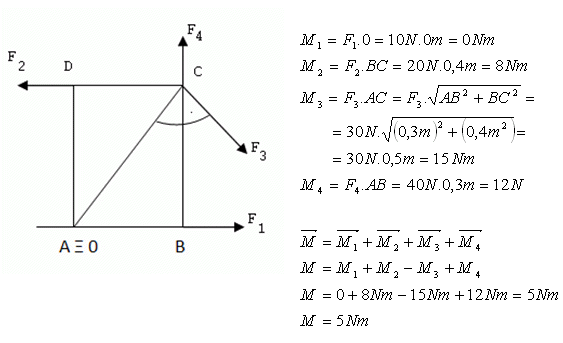
The resultant moment of the forces is 5 N·m.
3.A rectangular plate with dimensions a = 20 cm, b = 10 cm is mounted so that it can rotate about an axis passing through its center O perpendicular to the plate. Force F1 = 800 N. Calculate the magnitude of force F2 so that the plate remains at rest.
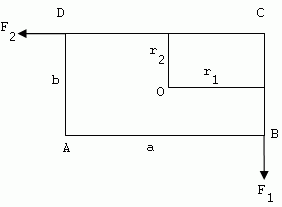
Solution:
Analysis:
a = 20 cm = 0.2 m, b = 10 cm = 0.1 m, r1 = 0.1 m, r2 = 0.05 m, F1 = 800 N
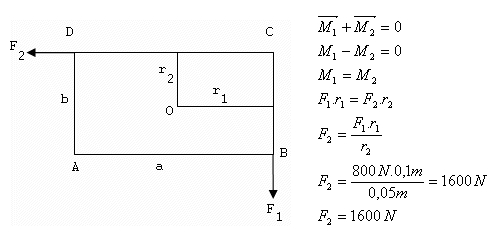
For the plate to remain at rest, the force F2 must be 1600 N.
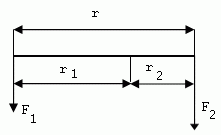
4.The rod has length 1.2 m. Weights of mass 5 kg and 7 kg are hung on its ends. Where should the rod be supported so that it remains in equilibrium?
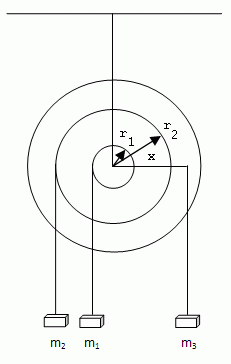
5.On a rotating pulley, weights m1 = 0.5 kg at distance r1 = 0.2 m and m2 = 0.2 kg at distance r2 = 0.4 m from the axis of rotation are hung on the same side of the rotation axis. At what distance from the axis must we hang a weight m3 = 0.6 kg on the other side so that equilibrium occurs?
6.How much work must we perform to spin a steel cylinder of mass 800 kg and base radius 0.5 m up to 48 revolutions per minute? Moment of inertia of a solid cylinder: (Tables)
Please log in to view the solution.
7.What is the moment of inertia of a flywheel if, during braking by work of 1260 J, its rotations drop from 320 min-1 to 254 min-1?
Please log in to view the solution.
8.A steel disc was spun using a rope of length 80 cm on which a force of 30 N acted. How many revolutions will it make in 1 second if its moment of inertia is 0.03 kg·m2?
Please log in to view the solution.
9.To what height would a toy car climb up a hill if it is driven only by a flywheel with moment of inertia 0.1 kg·m2? The flywheel makes 4 revolutions per second. The mass of the toy car is 8 kg.
Please log in to view the solution.
10.Determine the minimum frequency that a flywheel with moment of inertia 305 kg·m2 must reach so that over a time of 10 minutes it delivers power of 25 kW.
Please log in to view the solution.
11.
Explain when we use Steiner's theorem (the parallel-axis theorem) in the calculation of the moment of inertia of a rigid body?
Please log in to view the solution.
12.Calculate the moment of inertia of a solid homogeneous sphere with radius r = 10 cm and mass 25 kg with respect to an axis that is tangent to the surface of the sphere.
13. Determine the length of the rod l whose mass is 1.2 kg and modulus of inertia is 0.592 kg·m2, if the rod rotates at a distance 0.4 m from the fixed axis.
Please log in to view the solution.
14.A solid wheel (circular disc) of mass 20 kg and radius r = 50 cm rolls with speed 10 m·s-1. What is its kinetic energy?
Please log in to view the solution.
15.
What speed does a sphere gain when it rolls down an inclined plane from a height of 1 m?
Please log in to view the solution.