Special theory of relativity
1. Explain the difference between classical physics and the special theory of relativity,
Solution:
Classical physics (Archimedes, Newton) studies the physical properties of bodies that are relatively large and move at low speeds (v << c). It considers mass, length, time, simultaneity of two events, momentum, and energy as constant, independent of the speed of motion.
The special theory of relativity (Einstein) studies the motion of bodies that move at speeds comparable to the speed of light in a vacuum c.
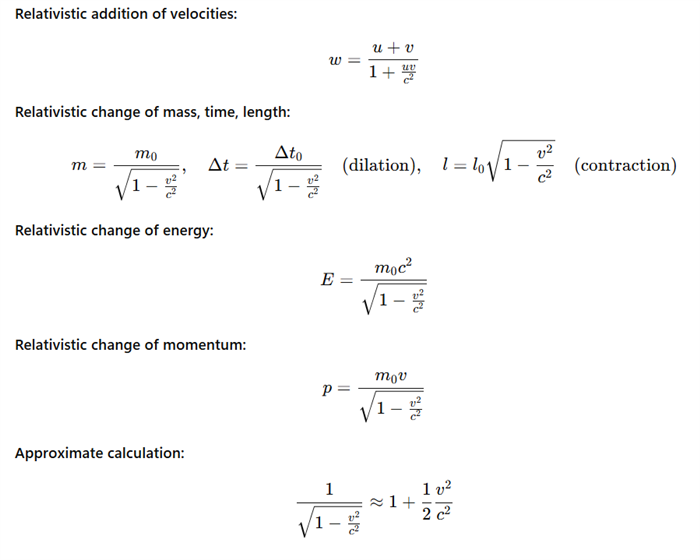
2. From an electron source, two electrons fly out in opposite directions. Each electron has a speed v1 = v2 = 0.8c relative to this gun. What is their relative speed?
Solution:
Analysis:
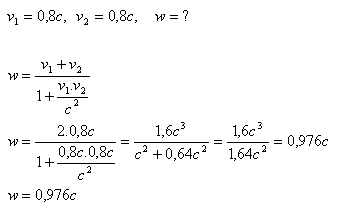
The relative speed of the electrons is w = 0.976c.
3. An α particle flew out of a laboratory accelerator with speed v and moved uniformly in a straight line. It passed through a tube of length 12 cm in 10 ns. What is the length of the tube in the reference frame attached to the α particle?
Solution:
Analysis:
s = 12 cm = 0.12 m, t = 10 ns = 10-9s, l = ?
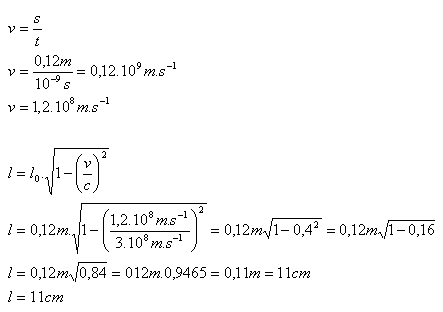
The length of the accelerator tube contracted to 11 cm.
4. A beam of π mesons flies out of an accelerator at speed v = 0.8c. The half-life of π mesons is t0 = 1.8·10-8s. Calculate the time it takes for half of the mesons to decay and the distance they travel before decaying.
Please log in to view the solution.
5. The density of iron is ρ0 = 7400 kg·m-3 in the rest frame. How does the density of an iron body change if its speed increases from zero to v = 0.5c?
Please log in to view the solution.
6. Calculate the speed at which the relativistic momentum of an α particle is twice as large as the momentum calculated according to the rules of classical mechanics.
Please log in to view the solution.
7. A spaceship moves relative to Earth at a speed of 12,000 km·s-1. How long does an event that lasts 1 hour on Earth take for an observer in the spaceship?
Please log in to view the solution.
8. What is the wavelength of a photon whose energy equals the energy of an electron moving at v = 0.6c?
Please log in to view the solution.9.The star is approaching Earth with speed v. At what speed does the light from this star travel through space for an observer on Earth?
Please log in to view the solution.
10.In a “cosmic train” moving through space with speed v1 = c/2, an astronaut moves with speed v2 = c/4 along the “train”. What speed will an observer standing outside the “train” measure if the astronaut moves
- a.) in the same direction as the “train”
- b.) in the opposite direction to the “train”
11.A hyperon moves in a bubble chamber with speed v1 = 0.8c and, when decaying into a proton, electron, and antineutrino, emits in the direction of its motion a proton that in the rest frame of the hyperon moves with speed v2 = 0.3c. What speed will the proton have with respect to the coordinate system of the bubble chamber if
- a.) the relativistic velocity-addition formula does not apply
- b.) the relativistic velocity-addition formula does apply
12.A school lesson on Earth lasts 45 minutes. How many minutes would the lesson last on a spacecraft, from the perspective of an observer on Earth, if the spacecraft is receding from Earth with speed v = 0.6c?
Please log in to view the solution.13.What speed must a rocket have relative to Earth so that a certain process observed on Earth is observed by the astronaut in the rocket as twice as long?
Please log in to view the solution.14.The mean lifetime of a meson is Δt0 = 2.2·10–6 s. Calculate the distance the meson travels from its creation to its decay into an electron and neutrino. The meson moves with speed v = 0.96c.
Please log in to view the solution.15.The distance of the star Proxima Centauri from Earth is 4.28 ly (light-years). What distance will be measured by an observer in a spacecraft that travels from Earth to the star with speed v = 0.8c relative to Earth?
Please log in to view the solution.16.A body that has the shape of a cube in its rest frame moves uniformly in the direction of the x-axis with speed v = 0.95c perpendicular to a face of the cube. The rest length of the cube is a0 = 1 m. Determine the volume of the body in the frame with respect to which the body is moving.
Please log in to view the solution.17.What was the rest length of a rod that moves relative to an observer at rest with speed v = 2.7·108 m·s–1? The observer sees the rod as 2.61 m long.
Please log in to view the solution.18.An elementary particle moves with speed v = 0.8c. What is the ratio of its mass to its rest mass?
Please log in to view the solution.19.An electron has been accelerated by a cyclotron so that its relativistic mass has become 5 times larger than its rest mass. What speed does the electron have?
Please log in to view the solution.
20.Derive the relativistic relation:
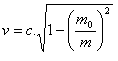
21.A proton has rest energy E0 = 933 MeV and moves with speed v = 0.5c. Calculate its relativistic kinetic energy.
Please log in to view the solution.22.At what speed does the kinetic energy of a particle equal its rest energy?
Please log in to view the solution.23.The mass of an accelerated electron increased 41 times. What energy did the electron gain during this acceleration?
Please log in to view the solution.24.What is the wavelength of a photon whose energy is equal to the rest energy of an electron?
Please log in to view the solution.25.An electron with rest mass m0 = 9.1·10–31 kg moves with speed v = 0.6c. Calculate the relativistic momentum of this electron.
Please log in to view the solution.