States of matter
1.Explain the states of matter and their changes!
Solution:
Substances can exist in three states (phases) – solid, liquid, and gas.
Melting – change from solid to liquid
Freezing – change from liquid to solid
Evaporation – change from liquid to gas
Boiling – evaporation occurring when the vapor pressure equals the external pressure
Condensation – change from gas to liquid
Sublimation – direct change from solid to gas
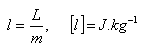
L = latent heat (melting, freezing, evaporation, boiling ...)
l = specific latent heat (melting, freezing, evaporation, boiling ...)
m = mass of substance
For ice – water – steam applies:
t melt = t freeze = 00C, t boil = t condense = 1000C,
l melt = l freeze = 334.103J.kg-1, l boil = l condense = 2260.103J.kg-1
l evap(200C) = 2430.103J.kg-1, l sub = 2830.103J.kg-1
c(H2O) = 4180 J.kg-1.K-1, c(ice) = 2100 J.kg-1.K-1
Conversion of ice to steam: Q = Q1 + L1 +Q2 + L2 + Q3
Q1 = heat needed to warm ice to melting point
L1 = heat needed to convert ice to water
Q2 = heat needed to warm water to boiling point
L2 = heat needed to convert water to steam
Q3 = heat needed to warm steam
2.Calculate the heat required to melt an aluminum object with a mass of 10 kg and an initial temperature of 200C. Use the tables.
Solution:
Analysis:
m = 10 kg, t1 = 200C, tm (Al) = 6600C, c(Al) = 896 J.kg-1.K-1
lm (Al) = 400.103J.kg-1
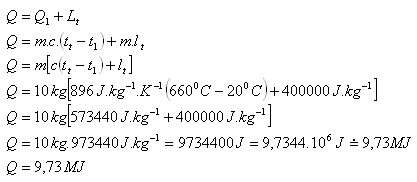
To melt the aluminum object, approximately 9.73 MJ of heat is required.
3.Determine the specific latent heat of fusion of copper if it is known that melting 5 kg of copper heated to its melting point requires 1.02 MJ of heat.
Solution:
Analysis:
m = 5 kg, L = 1.02.106J,
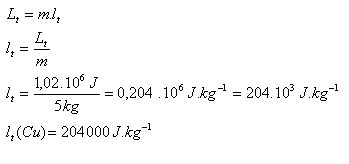
The specific latent heat of fusion of copper is lm (Cu) = 204,000 J.kg-1
4.Ice is placed into 5 liters of water at 500C. What must be the mass of this ice so that it all melts and the final water temperature after melting is 00C? Use the tables!
Please log in to view the solution.5.Water with a mass of 10 kg and a temperature of 00C is heated to 1000C and then completely evaporates into steam at the same temperature. What total heat did the water receive? What percentage of this heat is for heating the water and what percentage is for the change of state? Use tables!
Please log in to view the solution.6.A brass object has a mass of 500 g and a temperature of 200C. Calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of brass, knowing that melting this object requires 2,67·105 J of heat. The melting temperature of brass is 9700C and the specific heat capacity c(brass) = 394 J.kg-1K-1
Please log in to view the solution.
7.A brass body with a mass of 1 kg received heat of 441 980 J, as a result of which part of the brass with a mass of 500 g melted. What was the initial temperature of the body?
Please log in to view the solution.8.Determine the mass of coal with a calorific value of 30·106 J.kg-1 that must be burned in a boiler (η = 70%) so that water with a mass of m1 = 6·103 kg and temperature t1 = 100C is heated to t2 = 1000C and at this temperature an additional m2 = 103 kg of water evaporates.
Please log in to view the solution.
9.What is the minimum speed of a lead ball so that, upon impact on a steel plate, it completely melts? The temperature of the ball before impact was 270C. ( tt = 3270C, lt = 22 600 J.kg-1, c = 125 J.kg-1K-1)
Please log in to view the solution.
10.Draw the phase diagram for ice – water – steam. Characterize:
- a.) all four regions of the diagram
- b.) the triple point and the critical point
- c.) saturated and superheated steam
11.During heat exchange taking place at normal pressure, ice with a mass of 2 kg and an initial temperature of −100C melted. The resulting water was heated to 1000C and at this temperature it completely evaporated. Calculate the total heat that the system received.
Please log in to view the solution.
12.Water with a mass of 8 kg and a temperature of 120C condensed water vapour into it, causing the temperature of the water to rise to 600C. Determine the mass of the condensed steam.
Please log in to view the solution.
13.240 grams of saturated steam desublimates in such a way that every minute 12 kJ of heat is released. How long did the desublimation last?
Please log in to view the solution.
14.A lead body with a mass of 1 kg received heat of 54 500 J, as a result of which part of the lead with a mass of 0,5 kg melted. What was the initial temperature of the body?
Please log in to view the solution.
15.Calculate the mass of ice at a temperature of −200C that will melt in water with a mass of 1 kg at a temperature of 300C, if the final equilibrium temperature is 200C.
Please log in to view the solution.
16.On an electric cooker with a power of 600 W and an efficiency of 60%, water with a mass of 2 kg and an initial temperature of 100C was heated to a temperature of 1000C. At this temperature, 5% of the water evaporated. How long did the heating of the water last?
Please log in to view the solution.
17.Steam with a mass of 0,1 kg and a temperature of 1000C condenses in water with a mass of 2 kg and a temperature of 180C. What is the final temperature of the water?
Please log in to view the solution.
18.An ice cube has a mass of 10 grams and a temperature of 00C. In a calorimeter there is water with a mass of 1 kg and a temperature of 500C. How many ice cubes must we put into the calorimeter so that all the ice melts and the final temperature of the water in the calorimeter is 00C? (Neglect losses.)
Please log in to view the solution.
19.What energy is released when a pond with an area of 1 ha freezes if an ice layer 10 cm thick forms on it? The initial temperature of the water is 00C and the resulting ice also has a temperature of 00C.
Please log in to view the solution.
20.How does the internal energy of water with a mass of 300 grams and a temperature of 200C differ from the internal energy of water vapour with the same mass and temperature?
Please log in to view the solution.