Work in an electric field
1. Characterize the physical quantities: work in an electric field, electric potential and electric voltage.
Solution:
A)
Work in an electric field is the work of external forces when moving a charge in the electric field.
intensity of the electric field, moved charge,
distance the charge is moved
B)
The electric potential at a given point in the electric field is the ratio of the work performed by the electric forces of the electric field when moving a particle with charge from that point to the point of zero potential and the charge .
C)
The electric voltage between two different points of the electric field is equal to the absolute value of the difference in potentials between these points of the electric field.
2.What amount of work does an electric field of intensity 104N.C-1 perform when it moves a charge of 20 μC along the field line for a distance of 10 cm.
Solution:
Analysis:
E = 104N.C-1, Q0 = 20 μC = 20.10-6C, d = 10 cm = 10-1m
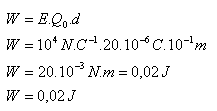
The electric field does work W = 0,02 J
3.What is the potential of a conductor if transferring a charge of 50 μC from a point of zero potential to its surface required work of 0.2 J?
Solution:
Analysis:
Q0 = 50.10-6C, W = 2.10-1J, φ = ?
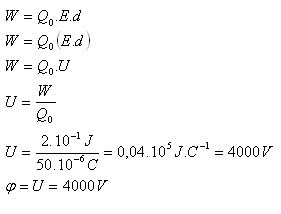
The conductor has potential φ = 4000 V.
4.In a homogeneous electric field with intensity 1 kV.m-1, a particle with charge 25.10-9C moves along a path of 2 m.
- a) What work do the forces of the electric field perform when moving the particle?
- b) What is the electric voltage between the starting and ending points of the displacement?
5.What speed will an electron (Qe= 1,602.10-19C, me = 9,1.10-31kg) reach when passing through a potential difference of 100 V?
Please log in to view the solution.
6.Determine the intensity of the electric field between two parallel conducting plates separated by 5 cm if the voltage between them is 150 V. What work do the field forces perform when transferring a charge of 1 μC from one plate to the other?
Please log in to view the solution.
7.An alpha particle ( mα = 6,7.10-27kg, Q0α = 3,2.10-19C) entered a homogeneous electric field with velocity 2.106m.s-1. The particle stopped after travelling 2 m.
- What potential difference did the particle traverse?
- What is the magnitude of the electric field intensity?
8.What electric charge does a microscopic oil droplet of mass 6,4.10-16kg have if it hovers between the plates of a charged capacitor? The capacitor plates are 1 cm apart and the voltage between them is 400 V. (Experiment R.A. Millikan)
Please log in to view the solution.
9.What work do the forces of the electric field created by charge Q = 2 μC perform when moving charge Q0 = 1 nC from a point 10 cm from charge Q to a point 20 cm from charge Q.
Please log in to view the solution.
10.An electron (e = 1,602.10-19C) moves in a homogeneous electric field from a potential level of 200 V to a level of 300 V. The initial speed is zero, the final speed is 5,93.106m.s-1. Determine:
- the increase in the electron's energy as it passes between the two potential levels
- the mass of the electron
11.Determine the magnitude of the electric field intensity between two parallel conducting plates if transferring a charge of 8·10-6C from the negative (grounded) plate to the positive one requires work of 2 J. The distance between the plates is 25 cm.
Please log in to view the solution.12.Derive additional formulas for potential, voltage, and electric field intensity.
Please log in to view the solution.13.What work is done by the forces of the electric field of a point charge Q = 10–8C when transferring a charge Q0 = 10–6C from a point 3 cm away to infinity?
Please log in to view the solution.14.What is the potential of a conductor if transferring a charge of 50·10-6C from a point of zero potential to its surface required work of 0.2 J?
Please log in to view the solution.15.Two point charges 0.1·10-6C and 0.2·10-6C are 20 cm apart. What is the potential at the midpoint between them?
Please log in to view the solution.16.Two charges 0.1·10-6C and 0.2·10-6C are 20 cm apart. What is the electric field intensity at the midpoint between them?
Please log in to view the solution.
17.Twenty-seven drops of water (r) merge into one larger drop (R). Determine the potential of the larger drop if each smaller drop had a radius of 1 mm and charge Q0 = 10-10C.
Please log in to view the solution.18.A small sphere with mass 40 micrograms, charged with a positive charge of 10–9C, moves at a speed of 10 cm·s-1. What is the minimum distance to which the sphere can approach a positive point charge of 1.33·10–9C?
Please log in to view the solution.19.A positively charged spherical conductor with radius 5 cm creates at a point 1 m from the center of the sphere an electric field of 1 V·m-1. What is the potential of the spherical conductor?
Please log in to view the solution.20.The distance of a given point from a positive point charge Q increases by a factor of 4. How does the electric field intensity change and how does the electric potential change?
Please log in to view the solution.