Ionic equations
Ion is an atom or a molecule with a nonzero charge, meaning the total number of its electrons does not equal the number of its protons. The tendency to form ions depends on the electronegativity of each element. If the number of electrons exceeds the number of protons, the atom or molecule is negatively charged. Such a particle is called an anion. If the number of protons exceeds the number of electrons, the particle is positively charged and we call it a cation.
Ions are distinguished as monoatomic (Na+, Cl-, Cu2+, Ir3+…), molecular (OH-, CO32-, HS-…) and complex ([Fe(CN)6]4-, [Cu(H2O)6]2+, [Cu(H2O)2(NH3)4]2+, [HgI4]2-…)
Ionic equations are chemical equations that describe reactions of ions in aqueous solutions of acids, bases, and salts. For these reactions to take place, at least one of the following conditions must be met:
- A precipitate (insoluble substance) is formed
- A weak electrolyte is formed
- A gas is formed
- The oxidation number of atoms changes
We write weak electrolytes (NH4OH, H2S, HCN, H2O…), gases (CO2, SO2, SO3, NH3, Cl2, NO…) and precipitates (AgBr, CaCO3, AgCl, PbI2…) as whole molecules.
1. Write the given chemical equation in ionic form:
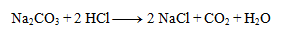
Solution:
We can write as ions only formulas of strong acids, bases, and salts well soluble in water. Other substances are not dissociated:
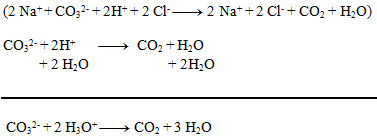
2.
Write the ionic equation of the precipitation reaction of sulfuric acid with barium chloride.
Solution:
First, we write the equation in stoichiometric form:
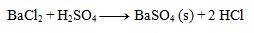
Next, we write the dissociations:
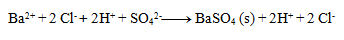
Final equation:
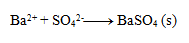
3.
The following equations are precipitation reactions. Write them in ionic form:
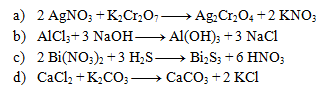
Solution:
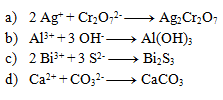
4.
The following equations represent complex formation reactions. Write them in ionic form:
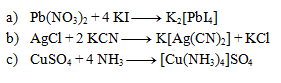
5.
Balance the following ionic equations. Pay attention not only to the sum of atoms but also to the sum of charges on both sides.
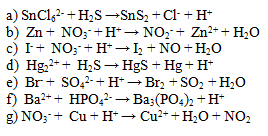
6. Write the ionic equation and the net ionic equation of the reaction of sodium chloride with silver nitrate.
Please log in to view the solution.7. Determine the stoichiometric coefficients in the following chemical equation:
[SnCl3]– + H2O → [Sn3(OH)4]2+ + H3O+ + Cl–
8. The reaction of barium chloride with magnesium sulfate produces a precipitate of barium sulfate. Write the net ionic equation of this process.
Please log in to view the solution.9. Dissolving calcium phosphate precipitate using nitric acid can be written as:
Ca3(PO4)2↓ + 6HNO3 → 3Ca(NO3)2 + 2H3PO4
Write the ionic and net ionic equations for this reaction.
10. Write the ionic equation of the reaction of sodium hydroxide with sulfuric acid.
Please log in to view the solution.11. Balance the following ionic reactions and make sure to preserve the overall charge of reactants and products, not just stoichiometry:
P3- + H2O → PH3 + OH-
Au3+ + Cl- → [AuCl4]-
As2S3 + OH- → AsO2- + AsS2- + H2O
[Cu(H2O)6]2+ + Cl- → [CuCl4]2- + H2O
VO43- + H+ → V3O93- + H2O
CrCl2O2 + OH- → CrO42- + Cl- + H2O
HPO42- + MoO42- + H+ → [P(Mo3O10)4]3- + H2O
[Al(H2O)4(OH)2]+ + CO32- → [Al(H2O)3(OH)3] + HCO3-