Molar volume (+ equation of state)
1. Calculate the volume occupied by 2.55 mol of methane at a temperature of 20°C and a pressure of 100.5 kPa.
Solution:
n = 2.55 mol; T = 20°C, which corresponds to 293.15 K; p = 100500 Pa; R = 8.314 J·mol-1·K-1
We solve the problem using the state equation rearranged into the form: 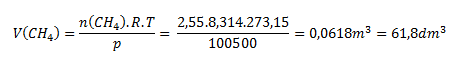
Under the given conditions, methane occupies a volume of 61.8 L.
2. A gas holder with a volume of 50.00 m³ contains hydrogen (H2) at a temperature of 25°C and a pressure of 101300 Pa. Calculate the amount of substance of hydrogen in the gas holder.
Solution:
V = 50 m3; p = 101300 Pa; R = 8.314 J·mol-1·K-1; T = 25°C which corresponds to 298.15 K.
We rearrange the state equation into the form: 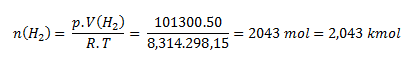
The gas holder contains 2.043 kmol of hydrogen.
3. The reaction produced 19.72 dm3 of acetylene under normal conditions. Calculate its amount of substance.
Solution:
We use the adjusted relation for the molar volume of a substance under normal conditions: 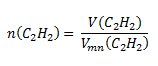
Substitute into the relation:
V (C2H2) = 19.72 dm3; Vmn (C2H2) = 22.41 dm3
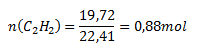
The reaction produced 0.88 mol of acetylene.
(The problem can also be solved logically. One mole of an ideal gas occupies 22.41 L. Our amount occupies only 19.72 L. To calculate the amount of substance, just take the ratio 19.72 / 22.41, which equals 0.88 mol.
This can also be shown in a proportion:
1 mol ..........................22.41 dm3
x mol...........................19.72 dm3
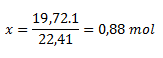
The reaction produced 0.88 mol of acetylene.
4. In a 20-liter pressure vessel, hydrogen is under a pressure of 101.97 kPa. Calculate how the pressure in the vessel changes
- a) when cooled from 20°C to -20°C
- b) when heated from 20°C to 50°C
5. By how much does the pressure of oxygen decrease if its volume is tripled at constant temperature?
Please log in to view the solution.6. The volume of a gas at 27°C is 50 ml. To what temperature must the gas be heated at constant pressure for the volume to increase to 200 ml?
Please log in to view the solution.7. The volume of hydrogen in a vessel above water at 27°C and a pressure of 107.59 kPa is 124 ml. Calculate the volume that dry hydrogen would occupy under normal conditions. The partial pressure of water vapor at 27°C is 3.59 kPa.
Please log in to view the solution.