Pyramid and Cone
1. Characterize the calculation of volume and surface area for:
- pyramid
- truncated pyramid
- cone
- truncated cone
Solution:
Pyramid (Sₚ = base, v = height, Q = lateral surface area)
Truncated pyramid (Sₚ₁, Sₚ₂ = lower and upper base, v = height, Q = lateral surface area)
Cone (r = base radius, v = height of the solid, s = slant height, Q = lateral surface area)
Truncated cone (r₁, r₂ = radii of the bases, v = height of the solid, s = slant height)
2. A regular square pyramid is given (the base is a square with side a).
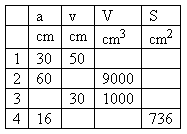
Solution:
For wall height apply: 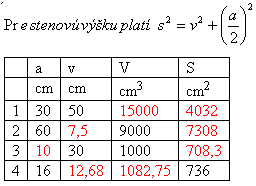
3. Above each face of a cube with edge a = 30 cm, a regular square pyramid with height 15 cm is constructed.
a) lie outside the cube
b) lie inside the cube
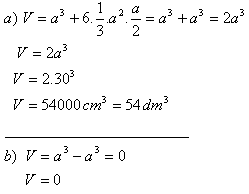
The volume of the solid in the first case is V = 54 dm3, in the second case it is zero.
4. Calculate the volume of a pyramid whose lateral edge of length 5 cm forms an angle α = 60° with the square base. (Angle α is the angle between the edge and the diagonal of the base.)
Please log in to view the solution.5. Determine the mass of a concrete pillar (ρ = 2.2 g.cm-3) in the shape of a regular square frustum of a pyramid, if its square bases have sides a = 45 cm, b = 25 cm, and the height of the pillar is v = 33 cm.
Please log in to view the solution.6. A cone with dimensions given in the table is given.
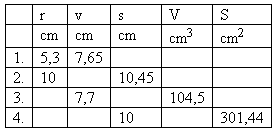
7. A right triangle with legs a = 3 cm, b = 4 cm rotates around the longer leg.
8. The surface area of a cone is S = 235.5 cm2. The axial section of the cone is an equilateral triangle.
9. The lateral surface of a cone, developed into the plane, has the shape of a circular sector with central angle α = 150° and area S = 523.4 cm2.
10. The surface area of a frustum of a cone is 7693 cm2, the radii of the bases are 28 cm and 21 cm.
11. The volume of a frustum of a cone is V = 38 000π cm3. The radius of the lower base is 10 cm larger than the radius of the upper base.
12. A frustum of a cone with radii x = 15 cm, y = 13 cm and height v = 9 cm was rolled out into a cylinder with radius r = 7.67 cm.