Interference of light
1.Explain the essence and methods of light interference.
Solution:
Interference arises from the superposition of two light waves, which must be coherent. They must have the same frequency and a constant phase difference. The coherence condition cannot be satisfied by light waves from two different
sources. It can be achieved by splitting the light wave from one source into two coherent waves. This can be achieved:
- a) by reflection of the wave from an obstacle – interference by reflection
- b) by diffraction of the wave behind an obstacle or a slit – interference by diffraction
Interference maximum – place where light is strengthened by interference
Interference minimum – place where light is weakened or cancelled by interference.
| Interference | maximum | minimum |
|---|---|---|
| By reflection | ||
| By diffraction |
k = 1,2,3,....
2.Determine the thickness of the wall of a soap bubble (n = 1.33) when white light falls on it. The first-order interference maximum is observed in green color (fG = 5.7·1014Hz).
Solution:
Analysis:
n = 1.33, fG = 5.7·1014Hz, c = 3·108m·s-1, d = ? k = 1
This involves using the relation for the first-order interference maximum by reflection.
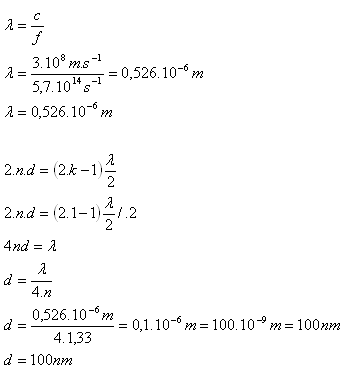
The thickness of the soap bubble wall is d = 100 nm.
3.The thickness of an oil film is d = 2.4·10-7m and the refractive index of oil is n = 1.5. Which colors of reflected light are cancelled out by interference?
Solution:
Analysis:
This is interference minimum by reflection.
d = 2.4·10⁻⁷ m, n = 1.5, λ = ?
k = 1 ⇒ – red light
k = 2 ⇒ – violet light
k = 3 ⇒ – ultraviolet radiation
By interference through reflection, red and violet light and invisible ultraviolet radiation are cancelled.
4.A glass plate with refractive index n = 1.5 and thickness d = 0.25μm is illuminated with light. What wavelength will be maximally strengthened in the reflected light?
Please log in to view the solution.
5.How many interference maxima are formed by diffraction of light on a grating with 5000 lines per 1 cm, when orange light with λ = 600nm falls on it?
Please log in to view the solution.
6.A diffraction grating with 100 lines per 1 mm is perpendicularly illuminated by red light (λ = 700nm). Determine the distance “h” between the first and third bright fringes on a screen that is at a distance l = 1.5m from the light source.
Please log in to view the solution.
7.How many lines per 1 mm does an optical grating have if light with wavelength λ = 589nm in the second maximum deviates from the direction perpendicular to the grating plane by an angle α = 43015‘?
Please log in to view the solution.
8.What must be the maximum thickness of an air layer in which it would be possible to observe, in light with wavelength 500 nm, an interference pattern created by the reflection of rays at the boundary of this layer?
Please log in to view the solution.9.Two coherent light waves with wavelength 600 nm meet at one point. Determine whether an interference maximum or minimum occurs there, if their phase difference is:
- a.) 300 nm
- b.) 600 nm
- c.) 900 nm
10. White light falls perpendicularly onto an oil layer of thickness d = 0.2 μm on water. The speed of light in oil is
v = 2·108 m·s–1. Which color is most intensified and which is cancelled in the interval λ : 3.8·10–7 m – 7.8·10–7 m?
11.Determine the thickness of a soap film (n = 1.33) at the places where we see the film as blue in reflected light. The wavelength of blue light is λ = 450 nm = 450·10–9 m = 4.5·10–7 m.
Please log in to view the solution.
12.Monochromatic light falls perpendicularly on a diffraction grating. On a screen at distance l = 1 m, a first-order maximum appears at distance h = 2 cm from the zero-order maximum. What is the wavelength of the light if
d = 20 μm?
13.A narrow beam of white light falls on a diffraction grating that has N1 = 1000 lines per 1 mm. How would the image on the screen change if we replaced the grating with another one that has N2 = 1500 lines per 1 mm?
Please log in to view the solution.14.A screen with very small openings whose centers are 1 mm apart is placed perpendicularly before a source of monochromatic light with λ = 500 nm. What is the spacing of the dark interference fringes formed on the screen? The distance from the openings to the screen is 2.5 m.
Please log in to view the solution.15.Monochromatic light with wavelength λ = 5·10–7 m falls on a diffraction grating that has 500 lines per mm. Determine the highest order of the spectrum that can be observed for perpendicular incidence on the grating.
Please log in to view the solution.16.What is the grating constant of a grating that, when illuminated with light of wavelength λ = 590 nm, forms a first-order maximum at distance h = 66 cm on a screen 2 m from the grating?
Please log in to view the solution.17.A diffraction grating with 100 lines per 1 mm is illuminated perpendicularly by a parallel beam of red light (λ = 700 nm). Determine the spacing between the 1st and 3rd bright fringes on a screen 100 cm from the grating.
Please log in to view the solution.18.A diffraction spectrum was obtained using a diffraction spectroscope. A second-order diffraction maximum appeared at angle α = 30°. The grating was illuminated by monochromatic light with wavelength λ = 5.76·10–7 m. Determine the grating constant. How many lines does the grating have per 1 mm?
Please log in to view the solution.