Magnetic induction
1.Explain the physical quantity “stationary magnetic field” and its characteristics.
Solution:
A stationary magnetic field is a time-invariant, constant magnetic field. It arises around a stationary permanent magnet or around a stationary conductor carrying a constant electric current. It is represented by magnetic induction lines (MIL).
1.) Magnetic Induction B
Where:
-
= force with which the magnetic field acts on a conductor carrying current
-
= electric current passing through the conductor
-
= active length of the conductor
-
= angle between the conductor and the magnetic induction vector
2.) Permeability of the Medium μ
| Medium | μᵣ |
|---|---|
| air | 1.0 |
| water | 0.999 |
| iron | 15,000 |
| Fe + Ni + Cu | 100,000 |
3.) Ampère’s Law
4.) Some Cases of Magnetic Induction
a) At a distance r from a straight conductor:
b) At the center of a circular loop with radius r:
c) Inside a long cylindrical coil (solenoid) with N turns per unit length l:
2.A conductor placed in a homogeneous stationary magnetic field perpendicular to the direction of induction lines with an active length of 5 cm carries a current of 25 A. The magnetic field exerts a force of 50 mN on the conductor. Determine the magnitude of the magnetic induction.
Solution:
Analysis:
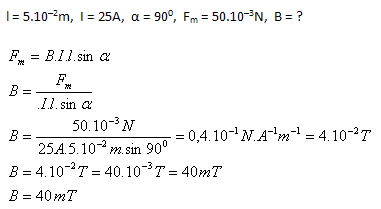
The magnetic induction of the field is B = 40 mT
3.A straight conductor of length 10 cm carrying a current of 2 A is acted upon by a force of 20 mN in a homogeneous magnetic field with magnetic induction of 0.2 T. Determine the angle between the conductor and the direction of the magnetic induction lines.
Solution:
Analysis:
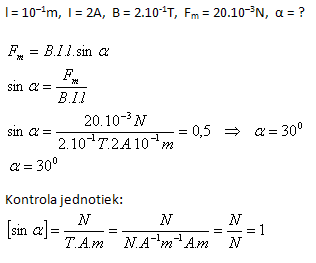
The angle between the conductor and the direction of the magnetic induction lines is 300.
4.A conductor carrying a current of 1 A with a cross-sectional area of 1 mm2 moves in a homogeneous magnetic field with constant acceleration of 2 m·s–2 perpendicular to the direction of induction lines. The density of the material of the conductor is 2500 kg·m3. Determine the magnitude of the magnetic induction.
Please log in to view the solution.
5.A straight conductor forming an angle α1 = 900 with the induction lines of a homogeneous magnetic field experiences a force greater by 0.134 N than when it formed an angle α2 = 600. Determine the magnetic induction of the field if the effective length of the conductor is l = 12.5 cm and it carries a current of 10 A.
Please log in to view the solution.
6.What electric current flows through a very long straight conductor if the magnetic induction at a distance of 20 cm from the conductor is 20 μT?
Please log in to view the solution.
7.What magnetic induction does the magnetic field of a solenoid of length 20 cm with 400 turns have, if the current passing through the solenoid is 5 A? What is the diameter of the wire from which the solenoid is wound, if the single-layer winding has turns placed directly next to each other?
Please log in to view the solution.
8.A straight conductor with current I formed an angle α with the induction lines of a homogeneous magnetic field. After changing its position, the conductor forms an angle α + 180 with the induction lines. The magnitude of the force acting on the conductor increased by 20%. Determine the angle α.
Please log in to view the solution.
9.A conductor of length l = 80 cm and mass m = 0.16 kg is suspended on two thin hanging wires and placed in a homogeneous magnetic field whose induction lines are directed vertically upward. Determine the angle α by which the hanging wires deviate from the vertical direction if a current I = 2 A flows through the conductor and B = 1 T.
Please log in to view the solution.10.A cylindrical coil without a core has the form of a long solenoid wound tightly with insulated wire so that adjacent turns touch each other. A current I = 0.5 A flows through the coil and inside it the magnetic induction has the value
B = 3.15 mT. Determine the diameter d of the wire from which the coil winding is made.
11.What is the magnitude of the force acting on a conductor of length 0.2 m placed in a homogeneous magnetic field, forming an angle α = 300 with the direction of the magnetic induction of the magnetic field? The magnetic induction is
B = 0.1 T, and a current I = 10 A flows through the conductor.
12.In a homogeneous magnetic field with magnetic induction B = 2 T, a force of magnitude F = 1.2 N acts on a conductor of length l = 20 cm, perpendicular to the induction lines. Determine the magnitude of the current in the conductor.
Please log in to view the solution.13.A force Fm = 1.8 N acts on the rotor winding conductor of an electric motor through which 20 A flows. Determine the magnetic induction at the location where the conductor is situated. The length of the conductor is 15 cm.
Please log in to view the solution.14.A straight conductor of length l = 50 cm through which a current I = 2 A flows is acted upon in a magnetic field with magnetic induction B = 0.1 T by a force Fm = 0.1 N. Determine the angle α that the conductor forms with the direction of the magnetic induction lines.
Please log in to view the solution.
15.Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic induction of the magnetic field in vacuum at a distance of 2 cm from a very long conductor carrying a current of 5 A.
Please log in to view the solution.16.A straight conductor of length 0.4 m carrying a current of 21 A lies in a homogeneous magnetic field with magnetic induction 1.2 T in a position perpendicular to the induction lines. Calculate the work that must be done to move the conductor along a path of 25 cm in a direction perpendicular to the induction lines.
Please log in to view the solution.
17.In a homogeneous magnetic field, a straight conductor is inserted perpendicular to the induction lines, parallel to the ground. The mass of the conductor is 0.75 kg, its length is 75 cm, and a current of 0.5 A flows through it. How large must the magnetic induction be for the conductor not to fall but to levitate?
Please log in to view the solution.
18.We need to wind a long cylindrical coil so that the magnetic field in the center of its cavity has magnetic induction not less than B = 8.2·10-3 T when a current I = 4.3 A flows through the coil. What should be the turn density of the coil?
Please log in to view the solution.
19.A circular loop surrounded by air has a radius of 1 cm. A current of 2 A flows through the loop. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic induction at the center of the loop.
Please log in to view the solution.20.A historical model representing the hydrogen atom consisted of a stationary nucleus and an electron orbiting around it on a circular path with radius r = 0.53·10–10 m and period T = 1.5·10–16 s. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic induction of the magnetic field excited by the motion of the electron along the circular path.
Please log in to view the solution.
21.What is the magnitude of the magnetic field intensity H from which a conductor of length l = 50 cm carrying a current of 10 A, positioned perpendicular to the induction lines, was pushed out by a force of 1 N?
Please log in to view the solution.