Energy
1.Briefly characterize the physical quantity energy.
Solution:
Energy is the ability of bodies to do work.
Energy:
- 1.) kinetic (motion) energy Ek
- 2.) potential (position) energy Ep
1.) Kinetic energy. Every body that is in motion has kinetic energy.
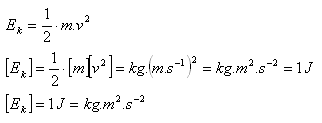
2.) Gravitational potential energy. Every body that is at a certain height above the Earth has potential energy.
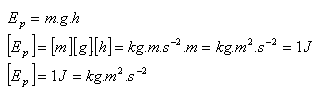
Law of conservation of mechanical energy:
In the isolated system body–Earth, the total mechanical energy is constant. At any moment, the sum of kinetic and potential energy is constant.
E = Ek + Ep = const.
2.A Ford Fusion car with a mass of 1156 kg increased its speed from 18 km·h-1 to 72 km·h-1. By how much did its kinetic energy increase?
Solution:
Given:
m = 1156 kg, v1 = 18 km·h-1 = 5 m·s-1, v2 = 72 km·h-1 = 20 m·s-1
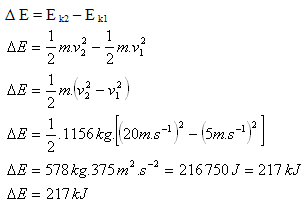
The car’s kinetic energy increased by ΔE = 217 kJ.
3.In what ratio are the kinetic energies of two balls if the second has twice the mass and four times the speed of the first?
Solution:
Given:
m2 = 2·m1, v2 = 4·v1
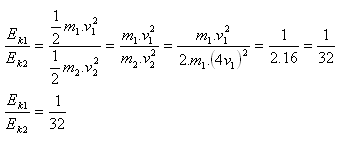
The kinetic energies are in the ratio 1 : 32.
4. A boat moves across a lake at a speed of 36 km·h-1. On deck a sailor of mass 80 kg walks at a speed of 2 m·s-1. Calculate his kinetic energy with respect to the lake if he walks
- a.) in the direction of travel
- b.) against the direction of travel
Please log in to view the solution.
5.A train with a mass of 200 tons moves at a speed of 54 km·h-1. When stopping, the brakes exert a force which, recalculated per each 1000 kg of the train’s mass, is 300 N. Determine:
- a.) the train’s kinetic energy before braking
- b.) the work the brakes must do to stop the train
Please log in to view the solution.
6.A weight of mass 2 kg is at a height of 50 cm above the surface of a table. The tabletop is 1.5 m above the room floor. Determine the potential energy of the weight
- a.) with respect to the tabletop
- b.) with respect to the room floor
Please log in to view the solution.
7.A ram of mass 400 kg falls from a height of 3 m. On impact it drives a stake to a depth of 60 cm. What is the magnitude of the average force overcoming the resistance of the soil?
Please log in to view the solution.
8.From a tower 45 m high, a stone of mass 300 g falls freely. Determine the total mechanical energy of the stone with respect to the Earth at the end of the first second of motion.
Please log in to view the solution.
9.Alpha particles are emitted during the radioactive decay of elements. They have a mass of 6.6·10-27 kg and a speed of 2·104 km·s-1. How many alpha particles will perform 1 J of work when braking in so-called “heavy water”?
Please log in to view the solution.
10. A mountain hut was damaged by a stone of mass 120 kg that originally hung 20 m above the hut. With what speed did the stone hit the hut? What would this speed be if the stone had a mass of 60 kg?
Please log in to view the solution.
11.A ball of mass 200 g swings on a thin thread. As it passes the lowest position it has a speed of 3 m·s-1. What maximum height will the ball reach when displaced?
Please log in to view the solution.
12. A body of mass 2 kg is thrown vertically upward. At a height of 15 m it has kinetic energy 450 J. To what maximum height will the body rise?
Please log in to view the solution.
13. A bullet of mass 6 g moving at a speed of 350 m·s-1 pierced a wooden board 20 cm thick and exited it with a speed of 150 m·s-1. Determine the mean value of the force with which the bullet acted on the board.
Please log in to view the solution.
14. A cart of mass 250 kg moves on horizontal rails at 2.4 m·s-1 and collides with an identical cart moving at 1.8 m·s-1. After the collision the carts stick together and continue moving jointly. Calculate what part of the mechanical energy is converted into other forms if the carts before the collision are moving
- a.) one behind the other
- b.) toward each other
Please log in to view the solution.
15.A railway wagon with a mass of 10 Mg hit a rigid buffer at a speed of 4 m·s-1. By what length is the wagon’s buffer spring compressed if its stiffness is 4 MN·m-1? (This uses elastic potential energy Ep = 1/2·k·y2, where k = spring stiffness, y = extension or compression of the spring.)
Please log in to view the solution.