Hydrodynamics
1. Let’s review some basic properties of fluid flow.
Solution:
Steady flow is such a motion of a fluid (gas) in which each particle moves in the same direction and with the same velocity.
It holds:
a.) Volumetric flow rate:
b.) Mass flow rate:
c.) Continuity equation:
d.) Bernoulli’s equation:
e.) Velocity of liquid outflow (Torricelli’s formula)
-
– distance of the opening in the vessel from the liquid surface
-
– distance of the opening in the vessel from the bottom
f.) Flow around a real body (Newton’s law)
Valid also for gases (air):
-
– drag coefficient (Tables)
2.A pipeline with variable cross-section carries 5 liters of water per second. What is the velocity of flowing water at sections with areas
- a.) S1 = 20 cm2
- b.) S2 = 100 cm2
Solution:
Analysis:
Q = 5 l.s-1 = 5 dm3.s-1 = 0.005 m3.s-1, S1 = 20 cm2 = 0.002 m2, S2 = 0.01 m2
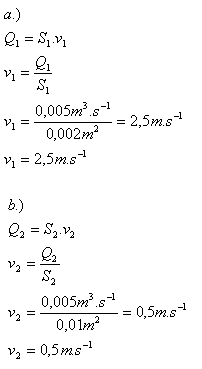
The velocities of flowing water are v1 = 2.5 m.s-1 and v2 = 0.5 m.s-1.
3.A small hydroelectric plant uses the energy of water flowing into a turbine from a height of 4 m. At what volumetric flow will the turbine have a power output of 600 kW if its efficiency is 75%?
Solution:
Analysis:
h = 4 m, P = 600·103 W, η = 0.75, ρ = 1000 kg.m-3, g = 10 m.s-2
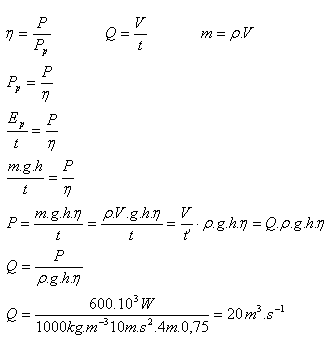
The turbine will have the required power at a volumetric flow Q = 20 m3.s-1
4.A pump delivers 300 l of water in 1 minute. The inlet pipe has a diameter of 80 mm, through the outlet pipe the water flows with a velocity of 8 m.s-1. Determine the velocity of water in the inlet pipe and the diameter of the outlet pipe.
Please log in to view the solution.5.In the wider part of a tube, water flows with a velocity v1 = 10 cm.s-1. What is the velocity in its narrower part, which has half the radius?
Please log in to view the solution.6.Diesel fuel (ρ = 830 kg.m-3) is transported through a pipe of diameter 40 cm at velocity 1.5 m.s-1. Determine
- a.) the hydrodynamic pressure in the pipe
- b.) the mass of diesel transported in 1 hour
7.In a horizontal pipe with diameter d1 = 5 cm, water flows at velocity v1 = 2 m.s-1 and pressure p1 = 2·105 Pa. What is the pressure in the narrower part of the pipe with diameter d2 = 2 cm?
Please log in to view the solution.8.In a water pipe, water flows with velocity 2.24 m.s-1 and has a pressure of 0.1 MPa. What is the velocity in the constricted part where the pressure is 0.09 MPa?
Please log in to view the solution.9.In the wall of a container filled with water, there is a hole 45 cm below the free surface. The container stands at the edge of a table so that the hole is 80 cm above the floor. At what distance from the table’s edge will the water jet hit the floor if the hole is opened?
Please log in to view the solution.10.A cylindrical container is filled with 18.84 liters of water per minute. At the same time, water flows out through a hole at the bottom with diameter 1 cm. At what height will the water level stabilize assuming ideal outflow of the liquid?
Please log in to view the solution.11. What drag hydrodynamic force acts on a sphere with radius r = 2.5 cm, if water flows around it with velocity 1.8 m.s-1. C = 0.48
Please log in to view the solution.12. With what velocity does a raindrop fall if its mass is 0.005 g, radius 2.26 mm. ρ (air) = 1.3 kg.m-3, C = 0.4
Please log in to view the solution.13.A submarine is subjected to a drag hydrodynamic force of 3600 N. The submarine has a frontal cross-section of 15 m2 and moves with velocity 14.4 km.h-1. Determine the drag coefficient C!
Please log in to view the solution.14.Calculate the terminal velocity of a parachutist with total mass 80 kg, if a hemispherical parachute has radius 5 m, drag coefficient 1.33, and air density 1.3 kg.m-3
Please log in to view the solution.15.
What is the radius of a glass bead (ρS = 2500 kg.m-3), if it falls in water (ρ = 1000 kg.m-3) with constant velocity v = 2 m.s-1. C = 0.48
Please log in to view the solution.