Hydrostatics
1.Let’s review the basic properties of an “ideal liquid.”
Solution:
An ideal liquid is a model of a liquid with the following properties:
- a) has no viscosity, it is perfectly fluid
- b) is a continuum – we do not consider its particle structure
- c) it is incompressible
The state of a liquid at a given point is determined by pressure p:
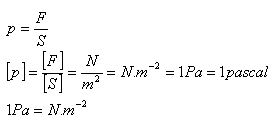
Pressure caused by an external force – Pascal’s law:
The pressure exerted by an external force acting on the surface of a liquid is the same at all points of the liquid.
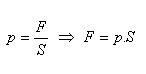
Pressure caused by the weight of the liquid – hydrostatic pressure
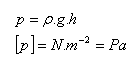
ρ – density of the liquid, g = 10 m.s-2, h – depth, distance from the surface
Hydraulic principle:
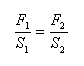
Archimedes’ principle:
A body immersed in a liquid is buoyed up by a hydrostatic buoyant force equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by the body.
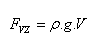
ρ – density of the liquid,
V – volume of the submerged part of the body
volume of displaced liquid
2.A piston with a diameter d = 20 cm lying on the surface of a liquid is subjected to a force F = 50 N. What pressure does this force create in the liquid?
Solution:
Analysis:
d = 20 cm = 0.2 m, F = 50 N, p = ?
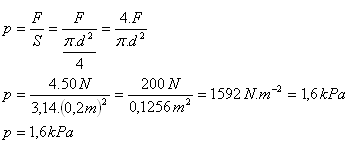
The force creates a pressure of about 1.6 kPa in the liquid.
3.Calculate the pressure of seawater (ρ = 1025 kg.m-3) at the sea bottom
- a.) at a depth of 3.6 km below the surface
- b.) at the deepest ocean trench, the Mariana Trench in the Pacific Ocean (h = 11 034 m)
Solution:
- a.) p = ρ.g.h = 1025 kg.m-3.10 m.s-2.3600 m = 36 900 000 Pa = 36.9 MPa
- b.) p = ρ.g.h = 1025 kg.m-3.10 m.s-2.11034 m = 113098500 Pa = 113.1 MPa
At a depth of 3.6 km the seawater pressure is 36.9 MPa, at the bottom of the Mariana Trench the pressure is 113.1 MPa.
4.People are used to air pressure of about 1013 hPa throughout their lives. To what depth can they dive into seawater (ρ = 1025 kg.m-3) without equipment?
Please log in to view the solution.
5.Into connected U-shaped vessels water (ρ1 = 1000 kg.m-3) and mercury were poured. The water in one arm reached a height of h1 = 100 cm, mercury in the other arm to h2 = 7.35 cm. Determine the density of mercury ρ2.
Please log in to view the solution.6.In a cylindrical container with base S = 100 cm2 there are 2 kg of mercury (ρ1 = 13 600 kg.m-3) and 1 kg of water (ρ2 = 1000 kg.m-3). Determine the hydrostatic pressure at the bottom!
Please log in to view the solution.7.Calculate the pressure force acting on the lid of a jar with diameter 8 cm, if the internal steam pressure is 2.5 kPa and the atmospheric pressure is 101325 Pa. (Assume the air inside the jar is completely evacuated.)
Please log in to view the solution.8.A tourist measured atmospheric pressure at the foot of a mountain: 1020 hPa, and at the top: 955 hPa. What altitude difference did the tourist overcome while climbing? (ρair = 1.3 kg.m-3)
Please log in to view the solution.9.A small hydraulic press has a piston diameter of 1.4 m, the pump piston diameter is 8 cm. What force acts on the press piston if the pump piston is subjected to a force of 4 N?
Please log in to view the solution.10.The radius of the circular base of the smaller piston of a hydraulic press is 4 cm. What radius must the larger piston have if a force of 80 N should generate a pressure force of 11 520 N?
Please log in to view the solution.11.The standard requires that in a submarine there must be on average 20 m3 of space per sailor. How many sailors can work in a submarine if, when submerged in seawater (ρ = 1020 kg.m-3), the buoyant force on the submarine is 15.3 MN?
Please log in to view the solution.12.A hydrometer has a volume of 150 cm3. How deep will it sink into a liquid of density ρ = 850 kg.m-3?
Please log in to view the solution.13.How much kerosene (ρ = 800 kg.m-3) must be poured into a barrel with a volume of 200 liters so that it would float completely submerged in water?
Please log in to view the solution.14.Can a wooden block of density ρ = 850 kg.m-3 sink to the bottom of a river if an iron chain of mass 1.5 kg is tied to it? The volume of the block is 0.01 m3.
Please log in to view the solution.15.A body of mass 800 g and volume 1.2 dm3 floats on the surface of water. What part of its volume sticks out above the water surface?
Please log in to view the solution.16.The volume of a hollow sphere is 8 liters, the mass is 4.5 kg. Will the sphere float in water?
Please log in to view the solution.17.What fraction of its volume is submerged in kerosene (ρ = 800 kg.m-3) if the body’s density is ρ = 600 kg.m-3?
Please log in to view the solution.18.
What is the pressure force of water on the bottom of a pool with dimensions 20 m × 12 m and depth 1.8 m?
Please log in to view the solution.19.A cuboid-shaped body of density ρ = 600 kg.m-3 and volume V = 0.01 m3 floats on water. What force is needed to immerse it completely below the water surface?
Please log in to view the solution.20.A block of volume V = 1.2 dm3 floats in water with 1/4 of its volume sticking out. What is its density?
Please log in to view the solution.21.A raft of mass m = 500 kg and volume V = 2 m3 floats on water. How many people of mass 75 kg can it carry, if at least 1/10 of its volume must remain above the water surface?
Please log in to view the solution.