Particle charge in a magnetic field
1. Explain the behavior of a charged particle in a magnetic field!
Solution:
If a particle with an electric charge (electron, proton, ion, …) enters a magnetic field perpendicularly to the induction lines, the magnetic field acts on the particle with a magnetic force
Fₘ = B·Q·v.
Under the influence of this force, the particle will move in the field with velocity v, whereby
it acquires a centrifugal force
F_OD = (m·v²) / r
If the forces are in equilibrium, the trajectory of the particle will be a circle with radius
r = (m·v) / (B·Q)
r = radius of the circular trajectory,
v = speed of the particle,
B = magnetic induction,
Q = electric charge of the particle.
It holds that:
If the particle moves in both an electric and a magnetic field, the Lorentz force applies:
F = Q·(E + v·B·sinα)
2. Derive the formula for the radius of the circular trajectory of a charged particle in a homogeneous magnetic field!
Solution:
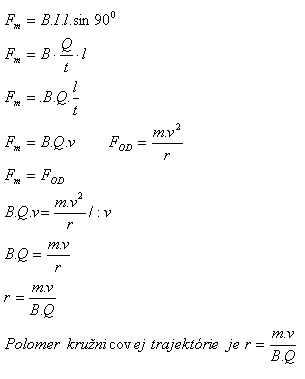
3. With what velocity did a proton (mp = 1.673·10–27kg, Qp = 1.602·10-19C) move in a magnetic field (B = 1T) if its trajectory was a circle with radius r = 60cm? With what frequency did the proton orbit the circle?
Solution:
Analysis:
mp = 1.673·10–27kg, Qp = 1.602·10-19C, B = 1T, r = 60cm = 0.6m, v = ?, f = ?
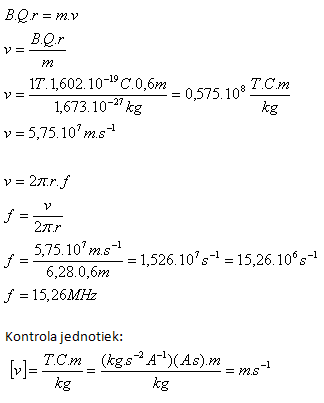
The velocity of the proton in the magnetic field was 5.75·107m·s-1, its frequency f = 15.26 MHz.
4. What kinetic energy does a proton (mp = 1.673·10-27kg, Qp = 1.602·10-19C) have when moving in a circle of radius r = 10cm in a homogeneous magnetic field with B = 0.1T, perpendicular to the induction lines?
Please log in to view the solution.
5. An electron (me = 9.1·10–31kg, Qe = 1.602·10–19C) after being accelerated in an electric field with U = 100V enters a homogeneous magnetic field with B = 10mT perpendicular to the induction lines. Along what trajectory will the electron move?
Please log in to view the solution.
6. What magnitude must the magnetic induction of a homogeneous magnetic field have so that an electron moves in it in a circle with radius r = 40cm at velocity v = 3.8·107m·s-1? What will be the kinetic energy of the electron?
Please log in to view the solution.
7. With what velocity would a proton (mp = 1.673·10–27kg, Qp = 1.602·10–19C) have to move in the Earth's magnetic field (B = 5·10–5T – tables) perpendicular to the induction lines so that the magnetic force equals the gravitational force acting on it?
Please log in to view the solution.
8. Into a homogeneous magnetic field with B = 2·10–5T in a vacuum entered a proton (mp = 1.673·10–27kg, Qp = 1.602·10-19C) in a direction perpendicular to the induction lines. What will be the frequency of its circular motion?
Please log in to view the solution.
9. Two electrons moving with the same velocities entered two homogeneous magnetic fields (B1 = 0.1T, B2 = 0.2T) and began moving in circular trajectories. Determine the ratio of their orbital periods T1 : T2.
Please log in to view the solution.
10. An electron started moving from rest and after passing through a potential difference of 220V entered perpendicularly into a homogeneous magnetic field with induction 5mT. In the magnetic field the electron moved in a circular trajectory with radius 1cm. Determine the mass of the electron.
Please log in to view the solution.
11.A proton moves in a homogeneous magnetic field. The magnetic induction of the field is B = 15 mT, the mass of the proton is mp = 1.67·10–27 kg, its charge is Qp = 1.602·10–19 C. Determine the radius of its circular path r, if the proton’s speed is v = 2·106 m·s-1.
Please log in to view the solution.
12.A particle with charge Q = 1.602·10-19 C entered a homogeneous magnetic field with magnetic induction B = 10-2 T. In this magnetic field it moves along a circle with radius r = 0.45·10-2 m. Determine the magnitude of the particle’s momentum.
Please log in to view the solution.
13.A proton moves at speed v = 1·106 m·s-1 in a homogeneous magnetic field with magnetic induction B = 1 T.
- What force acts on the proton (mp = 1.673·10–27 kg, QP = 1.602·10–19 C)
- Along what trajectory will the proton move?
14.An electron, after being accelerated in an electric field with U = 100 V, enters a homogeneous magnetic field with magnetic induction B = 10 mT perpendicular to the field lines. Along what trajectory will it move?
Please log in to view the solution.
15.What must be the voltage between the anode and cathode in a glass tube so that the luminous circular trace marking the trajectory of electrons has radius r = 5·10-2 m? The magnetic induction in the tube is B = 8.2·10-4 T.
Please log in to view the solution.
16.An α particle moves along a circular path with radius r = 4.5 cm in a homogeneous magnetic field with magnetic induction B = 1.2 T. Calculate:
- a.) its speed
- b.) its period of motion
17.A beam of protons moves in a vacuum tube such that their speed is v = 0.1c. The electrostatic force is Fe = 3·10–13 N.
- a.) What is the value of the ratio E/B if the net force acting on the proton is zero?
- b.) What is the magnitude of the magnetic induction B?
18.Between the anode and cathode of an electron gun in a vacuum cathode tube, electrons travel at speed v = 9.19·106 m·s-1. The distance between the plates is d = 1 cm with voltage U = 10 V. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic induction B of a homogeneous magnetic field for which the electrons will not be deflected from the axis of the tube.
Please log in to view the solution.
19.A proton and an α particle (mHe = 4·mp, QHe = 2·Qp) enter a homogeneous magnetic field perpendicular to the field lines. Compare the radii of the circular trajectories of the particles, if the particles have the same speed.
Please log in to view the solution.
20.An electron entered a homogeneous magnetic field with B = 10 mT perpendicular to the induction lines, with kinetic energy Ek = 30 keV. Determine the radius r of its circular trajectory.
Please log in to view the solution.