Radioactivity
1. What is radioactivity?
Solution:
Radioactivity is the transformation (decay) of atomic nuclei. The nucleus of one element gradually changes into the stable nucleus of another element, while energy is emitted. Natural radioactivity (M. Becquerel and P. Curie) is the spontaneous decay of unstable nuclei. Artificial radioactivity (I. and F. Joliot Curie) arises from artificially prepared nuclear reactions.
Natural Radioactivity
Displacement Rules:
Alpha decay:
Beta-plus decay (β⁺):
Beta-minus decay (β⁻):
Gamma decay (γ):
= electron,
= positron,
= neutrino,
= antineutrino
Law of Radioactive Decay:
= number of undecayed nuclei
= half-life — the time after which exactly half of the nuclei have decayed.
Law of Radioactive Transformation:
= number of decayed nuclei
2.Determine the sequence of radioactive transformations in the thorium decay series.
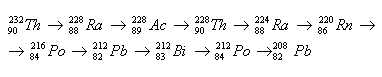
Solution:
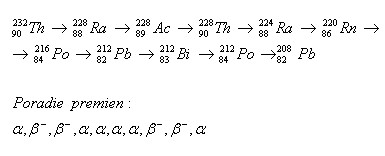
Order of transformations:
3. Determine the composition of the nucleus of the isotope of the element that arises from uranium.
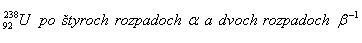
Solution:
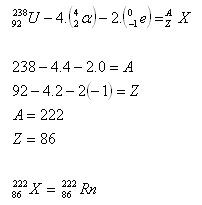
The element sought is an isotope of radon. [Determined using tables].
4.Complete the nuclear reaction equations:
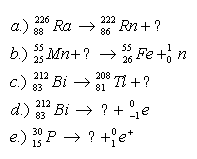
5.Determine the half-life of uranium if its decay constant is λ = 4.33·10-4 year-1.
Please log in to view the solution.
6.A nuclide has a half-life of 2400 seconds. What percentage of nuclei decay in 300 seconds?
Please log in to view the solution.
7.The number of decays in 1 gram of radium is 3.7·1010s-1. Determine the half-life.
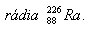
8.After what time will half of the nuclei of a radionuclide decay if its decay constant is λ = 1.42·10–11s-1?
Please log in to view the solution.
9.When determining the age of the burial boat from the tomb of Sesostris III, it was found that the concentration of carbon in the wood from which the boat was made is approximately N = 0.645·N0. N0 is the concentration of carbon in present-day living organisms. Determine the age of the burial boat if the half-life of carbon is 5730 years.
Please log in to view the solution.
10.In September 1991, tourists discovered in the Ötztal Alps in Austria an ice-mummified human body. Using the carbon method, it was found that for the undecayed nuclei in his body N and the nuclei in the bodies of present-day people N it holds that N = 0.5268·N0. How many years ago did this man freeze, if the half-life of carbon is T = 5730 years?
Please log in to view the solution.
11.The half-life of the nuclide radium is 1622 years. Determine its decay constant λ.
Please log in to view the solution.12.Radium has a half-life T = 1622 years. After what time will the number of radium nuclei decrease to 0.1% of the original number?
Please log in to view the solution.13.At present, 1 g of radium has 2.68·1021 nuclei. How many
- a.) undecayed nuclei
- b.) decayed nuclei after 4000 years?
-
14.During a time of 49.2 hours, the activity of radioactive sodium decreases to 0.1 of its initial value. What is the half-life of this nuclide?
Please log in to view the solution.15.The nucleus of uranium (Z = 92, A = 238) successively decays into other nuclei. In this decay chain there are 8 α decays and 6 β– decays. What is the final product of this decay series?
Please log in to view the solution.16.In a chain reaction, a neutron striking the nucleus 23592U induces fission of the nucleus into two medium–heavy nuclei and also releases several neutrons. How many neutrons are released in the following reaction?
Please log in to view the solution.17.Show that if λt << 1 holds, we can use the relation N/ = N0·λ·t to calculate the number of decayed nuclei.
Please log in to view the solution.18.A thin foil containing 1 gram of the nuclide thorium 23290Th emits 4100 α particles per second. Determine the half-life of this nuclide.
Please log in to view the solution.19.What percentage of the original amount of a radioactive element decays during a time equal to its mean lifetime?
Please log in to view the solution.20.At the beginning of the 20th century, prominent physicists discovered during experiments that a stable atomic nucleus can be broken apart by an external impact. This led to the discovery of artificial radioactivity. They succeeded in converting nitrogen into an isotope of oxygen, beryllium into carbon, and found a method to convert aluminum into phosphorus and then into silicon. In each of these experiments, a new elementary particle was discovered.
- WHICH ONE?