Electric current in semiconductors
1. The thermistor has a resistance of 50kΏ at a temperature of 200C and at a temperature of 250C its resistance decreases to 42.5kΏ. Determine the average value of the temperature coefficient of resistance in this temperature interval.
Solution:
Analysis:
Δt = 50C = 5K, R20 = 50 000Ώ, R25 = 42 500Ώ, α = ?
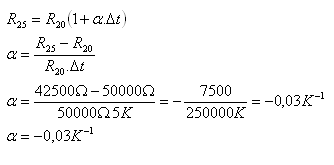
The temperature coefficient of resistance of the thermistor is α = –0.03K–1
2.The average value of the temperature coefficient of resistance of a thermistor is α = –0.05K–1. By how much must the temperature of the thermistor increase so that its resistance decreases to half?
Solution:
Analysis:
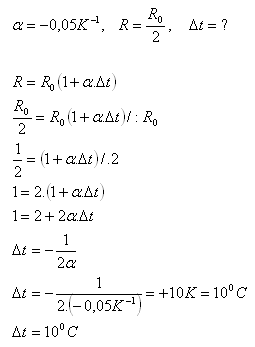
The temperature of the thermistor must increase by 100C.
3.A thermistor connected in an electric circuit is heated by the flame of a gas burner. The dependence of the thermistor's resistance on temperature is given by a table. What is the temperature of the thermistor if the reading on the voltmeter is 3V and on the ammeter 15mA?
Solution:
Analysis:
U = 3V, I = 15.10–3A
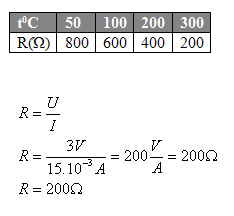
According to the table, the thermistor has a resistance of 200Ώ when heated to a temperature of 3000C.
4.An NPN transistor is connected in an electric circuit. If the base current changes from 0.2mA to 0.3mA, the collector current changes from 5mA to 20mA, at a constant collector voltage of 4.5V. Determine the current gain factor β of the transistor.
Please log in to view the solution.
5.A semiconductor sample cut from a silicon single crystal has the shape of a cuboid with a length of 5mm and a base area of 4mm2. On two opposite bases with an area of 4mm2 metallic contacts are formed. If a voltage of 4.5V is applied between the contacts, a current of 1.2mA flows through the sample at a temperature of 200C. After heating the sample to a temperature of 3000C the current increases to 2.16mA. What is the resistivity of silicon at temperatures of 200C and 3000C? Also determine the temperature coefficient of electrical resistance α.
Please log in to view the solution.6. The voltage on the thermistor has a constant value U = 4.5 V. At temperature t1 = 200C a current
I1 = 9 mA flows through the thermistor, at temperature t2 = 220C the current is I2 = 10 mA. Determine the values of the thermistor resistance at these temperatures and also the temperature coefficient of resistance α.
7.What is the current gain factor β of a transistor if a change of base current from IB1 = 0.1 A to IB2 = 0.2 A causes a change of collector current from IC1 = 6 A to IC2 = 22 A?
Please log in to view the solution.8.A transistor operating in a common-emitter configuration has a base current IB1 = 30 μA and collector current IC1 = 2 mA. Determine the collector current IC2 at a base current IB2 = 100 μA if the current gain factor is β = 60.
Please log in to view the solution.9.In electrical engineering practice, germanium is considered pure if there is at most 1 impurity atom per one billion (109) Ge atoms. Determine the mass of completely pure germanium that could be contaminated by one gram of iron. The relative atomic mass of germanium is 72.59 and of iron 55.837. Express the result in tonnes.
Please log in to view the solution.10.A transistor operating in a common-emitter connection conducts currents IB = 20 μA and IC = 2 mA. The voltage between the base and emitter is U1 = 0.7 V, and the voltage between the collector and emitter is U2 = 20 V. Calculate the power in both sources and compare them.
Please log in to view the solution.11.A resistor with resistance R and a thermistor are connected in series in a circuit. At temperature t1 the milliammeter shows current I1. If the thermistor is placed into hot oil, the milliammeter shows current I2. Determine by what factor the resistance of the thermistor changes after immersion in the oil. The voltage source has voltage U. Solve the problem for these values:
12.A sample of doped silicon in the shape of a cube with edge 1 cm contains 1014 phosphorus atoms. Two opposite faces of the cube are metal-coated and the sample is connected across a voltage of 4.5 V. A current of 108 mA flows through it. Calculate:
- a.) the density of free electrons in the sample at room temperature (the density of phosphorus atoms)
- b.) the resistivity