Electromagnetic oscillator
1. State the composition and properties of an electromagnetic oscillator.
Solution:
An electromagnetic oscillator is an alternating-current circuit with a coil (inductance) and a capacitor (capacitance). It is also called an oscillating circuit or an LC circuit. In an oscillating circuit, electrical energy is periodically converted into magnetic energy and back. Electromagnetic oscillations arise in the oscillating circuit. For the frequency of the electromagnetic oscillator (the oscillator’s natural frequency), Thomson’s relation applies:

2. How will the oscillation frequency of the LC circuit change if we move the plates of the capacitor closer together?
Solution:
If we move the plates of the capacitor in the oscillating circuit closer together, d decreases, C increases, and the frequency f decreases.
3.The oscillating circuits have parameters:
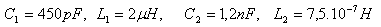
Which circuit oscillates at the higher frequency?
Solution:
Analysis:
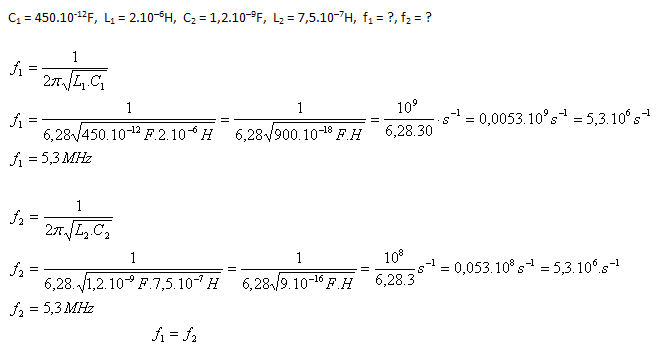
Both LC circuits oscillate at the same frequency, f1 = f2 = 6.3 MHz.
4.An oscillating circuit consists of a capacitor with capacitance C = 10 μF and a coil with variable inductance. Over what interval must the coil’s inductance vary so that the circuit’s natural oscillation frequency varies from 400 Hz to 500 Hz?
Solution:
Analysis:

The inductance of the coil must vary from L1 = 16 mH to L2 = 10 mH.
5.The oscillating circuit consists of a coil with inductance L = 3 mH and a parallel-plate capacitor whose plates are disks of radius 1.2 cm. The separation of the plates is 0.3 mm. Determine the period of the oscillating circuit. How does the period change if we insert a dielectric with εr = 4 between the plates of the capacitor?
Solution:
Analysis:
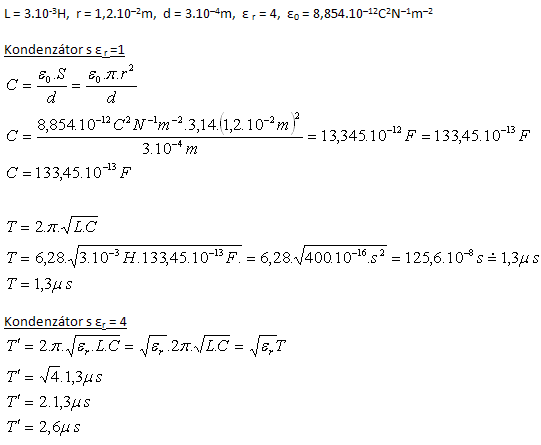
If we insert a dielectric with εr = 4 between the plates of the capacitor, the period of the circuit doubles.
6.We connect a capacitor with capacitance C1 to a coil with constant inductance L. We find that the oscillator oscillates with natural frequency f1 = 100 kHz. If we connect a capacitor with capacitance C2 to this coil, the oscillator will oscillate with natural frequency f2 = 160 kHz. What natural frequency will the oscillator have if we connect both capacitors to the coil
- a) in parallel
- b) in series
Solution:
Analysis:
f1 = 100 kHz = 105 s-1, f2 = 160 kHz = 1.6×105 s-1
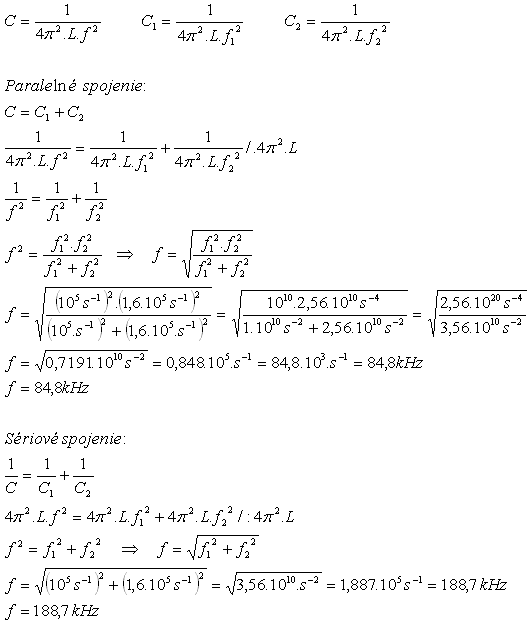
7.The voltage on the plates of a capacitor in an oscillatory circuit changes according to the equation u = 50cos (104π.t) (V). The capacitance of the capacitor is C = 0.1 μF. Calculate the oscillation period T of the circuit and write the equation for the instantaneous value of the current.
Solution:
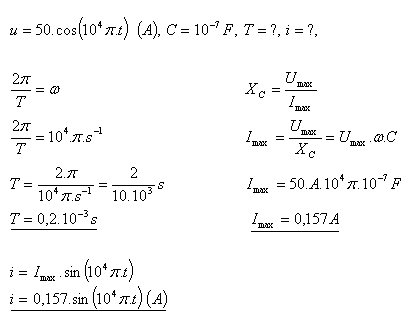
- The oscillation period of the circuit is T = 0.2·10–3s.
The equation for the instantaneous value of the current is i = 0.157sin (104π.t) (A).
8.The oscillatory circuit consists of a capacitor with capacitance C = 24 nF and a coil with inductance L = 0.6 H. At the initial moment, the capacitor is charged to the voltage Umax = 50 V. Write the equation for the instantaneous value of the current in the circuit.
Solution:
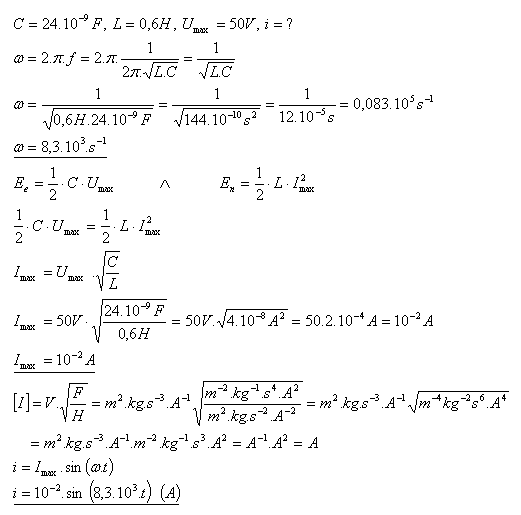
9.The instantaneous value of the current in an oscillatory circuit is given by the equation i = 0.01·sin (ω t) (A). Calculate the energy of the magnetic field of the coil at time t = T/8 s. The oscillatory circuit contains a coil with inductance
L = 0.6 H.
Solution:
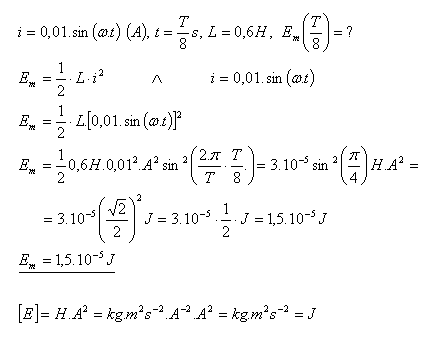
The energy of the magnetic field of the coil is Em = 1.5·10–5 J.
10.The instantaneous value of the voltage in an oscillatory circuit is given by the equation u = 50·cos (ω.t) (V). Calculate the energy of the electric field of a capacitor with capacitance C = 24 nF at time t = T/8 s.
Solution:
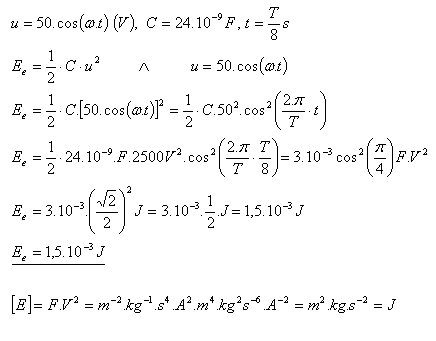
The energy of the electric field of the capacitor is Ee = 1.5·10–3 J.
11.An oscillatory circuit in which a coil (L) and a plate capacitor (C1) with plate spacing
d1 = 4.8 mm are connected is tuned to the wavelength λ1 = 300 m. How must the spacing between the capacitor plates be changed so that the oscillatory circuit is tuned to the wavelength λ2 = 240 m?
Solution:
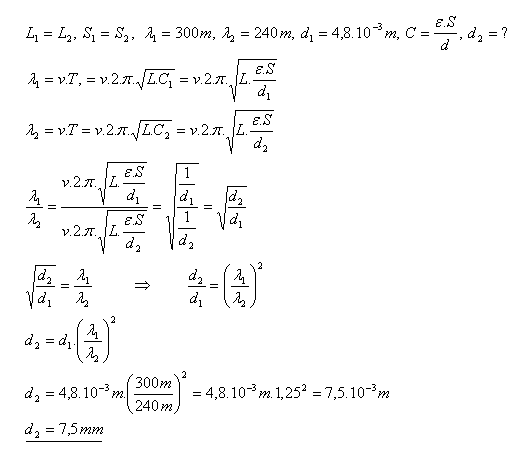
The distance between the capacitor plates must be increased to 7.5 mm.
12.The capacitance of the capacitors in the oscillatory circuit of a radio receiver can vary from C1 = C to C2 = 9C. Determine the range of wavelengths of the receiver if the minimum capacitance C1 corresponds to λ1 = 3 m.
(L1 = L2 = L)
Solution:
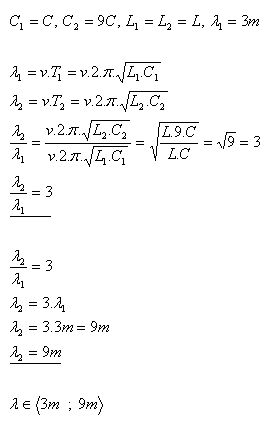
The wavelength range of the receiver is from 3 m to 9 m.
13.An oscillatory circuit whose capacitance is C = 4 μF has a frequency f1 = 200 Hz. If another capacitor with capacitance Cx is connected in parallel to the capacitor, the natural frequency decreases to f2 = 100 Hz. Calculate the capacitance of the added capacitor Cx.
Solution:
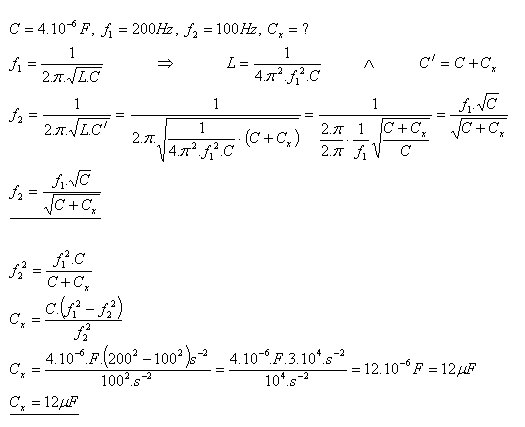
The capacitance of the added capacitor is Cx = 12 μF.
14.In an oscillatory circuit, a capacitor (C = 0.01 μF), a coil (L = 0.1 H), and a resistor (R = 1000 Ω) are connected in series. What is the ratio of the frequencies of the circuit with resistance and without resistance?
C = 10-8F, L = 10-1H, R = 103Ω, f1 = ?, f2 = ?
Solution:
Without resistance: With resistance: