AC Power
1.
Vysvetlite pojmy efektívne hodnoty striedavého prúdu a napätia a výkon striedavého prúdu.
Riešenie:
Meracími prístrojmi sa nemerajú okamžité ani maximálne hodnoty prúdu a napätia, ale „efektívne hodnoty“ prúdu a napätia.
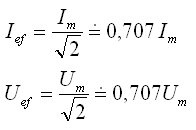
2. Rezistor s odporom 20Ώ je pripojený na zdroj striedavého napätia Uef = 24V a f = 50Hz. Napíšte rovnicu pre okamžitú hodnotu prúdu v obvode. Určite efektívnu hodnotu prúdu v obvode.
Riešenie:
Rozbor:
R = 20Ώ, Uef = 24V f = 50s-1, Ief = ?
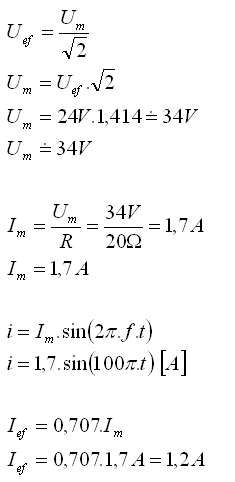
- Rovnica pre okamžitú hodnotu prúdu v obvode je i = 1,7.sin(100π.t) [A]
- Efektívna hodnota prúdu v obvode je Ief = 1,2A.
3.
Určite časové okamžiky v priebehu jednej periódy striedavého napätia, pri ktorých sa okamžité napätie rovná efektívnemu napätiu.
Riešenie:
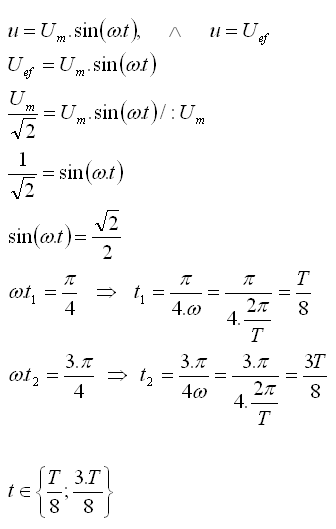
Okamžité napätie rovná sa efektívnemu napätiu pre t1 =T/8 a t2 = 3T/8.
4.
Striedavé napätie má efektívnu hodnotu Uef = 156V. Určite amplitúdu napätia. Za aký čas od začiatočného okamihu dosiahne okamžitá hodnota striedavého napätia efektívnu hodnotu, ak f = 50Hz.
Riešenie:
Rozbor:
Uef = 156V, f = 50Hz = 50s–1, Um = ?, t = ?
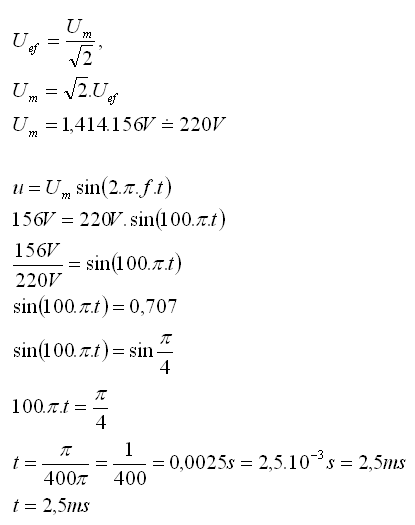
Okamžitá hodnota striedavého napätia dosiahne efektívnu hodnotu Za čas t = 2,5ms.
5.
Pre okamžité hodnoty prúdu a napätia v obvode striedavého prúdu platia rovnice i = 1.sin(100π.t – π/4) [A] a u = 150.sin(100π.t) [V] Určite činný, zdanlivý a jalový výkon tohto prúdu. Ukážte, že platí:
Riešenie:

6.
Vypočítajte činný výkon striedavého prúdu, ktorý je zapojený na zdroj striedavého prúdu (U = 220V, f = 50Hz, cos φ = 0,8), ak v obvode je zapojený spotrebič, ktorý má vlastnosti:
- a.) cievky s indukčnosťou L = 0,1H
- b.) kondenzátora s kapacitou C = 10-3F
Zistite, ako sa bude s frekvenciou meniť činný výkon striedavého prúdu.
Riešenie:
Rozbor:
U = 220V, f = 50Hz, cos φ = 0,8
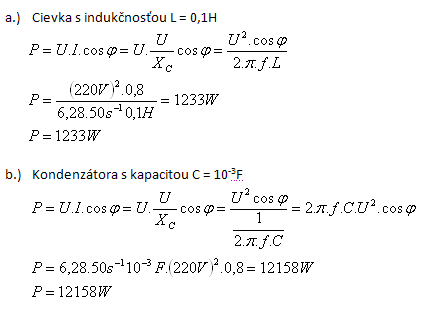
- Ak je v obvode zapojená cievka a frekvencia sa bude zväčšovať, činný výkon sa bude zmenšovať (f je v menovateli)
- Ak je v obvode zapojený kondenzátor a frekvencia sa bude zväčšovať, činný výkon sa bude tiež zväčšovať. (f je v čitateli)
7. Vypočítajte, aký prúd prechádza jednofázovým elektromotorom na striedavý prúd, ak má výkon 5kWa je napojený na elektrickú sieť o napätí 220V. Účinník elektromotora je 0,85 a jeho účinnosť 80%.
Riešenie:
Rozbor:
P = 5000W, U = 220V, cosφ = 0,85, η = 0,8
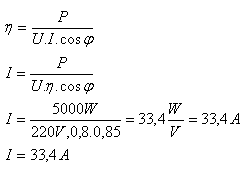
Jednofázovým elektromotorom prechádza prúd I = 33,4A
8. Pri napätí 48V prechádza obvodom prúd 6A. Činný výkon v obvode je 200W. Vypočítajte účinník. Posúďte, ako by sa zmenil činný výkon zariadenia, keby sa podarilo zlepšiť účinník na 0,98
Riešenie:
Rozbor:
U = 48V, I = 6A, P1 = 200W, φ1 = ?, cos φ2 = 0,98
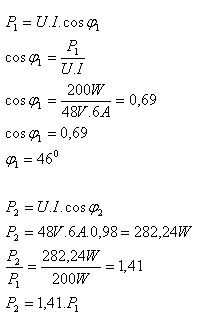
Činný výkon sa zväčší 1,41 krát. (o 41%)
9.Na striedavé napätie 3000V s f = 50Hz sú pripojené za sebou rezistor s odporom R = 40Ώ a cievka s indukčnosťou L = 95.10-3H. Určite prúd v obvode, fázový posun medzi prúdom a napätím a činný výkon prúdu.
Riešenie:
Rozbor;
U = 3000V, f = 50Hz, R = 40Ώ, L = 95.10-3H, I = ?, φ = ?, P = ?
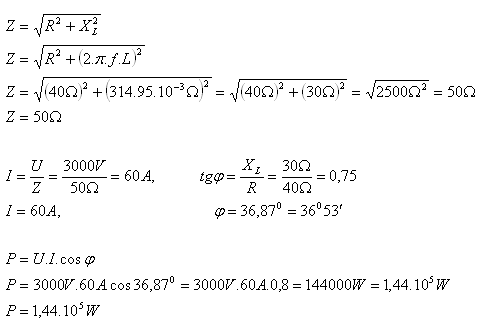
V obvode je prúd I = 60A, fázový posun φ = 36053‘ a činný výkon 1,44.105W.
10. Jednofázový motor odoberal za čas 5 minút prúd 10A pri napätí 220V. Elektromer za ten čas nameral 0,125 kWh. Určite účinník motora.
Riešenie:
Rozbor:
t = 5 min. = 300s, I = 10A, U = 220V, W = 0,125 kW.h (1kWh = 3,6.106J) W = 0,125.3,6.106J = 0,45.106J
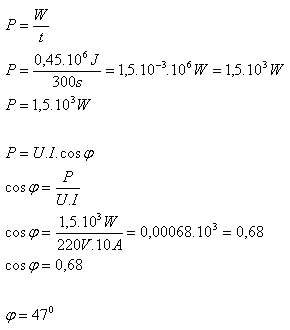
Účinník motora je cos φ = 0,68.