Varying magnetic field
1. State the basic characteristics of a non-stationary magnetic field.
Solution:
A non-stationary magnetic field is a time-varying magnetic field. The source of this field is a moving permanent magnet or electromagnet, a stationary conductor with a time-varying current, or a moving current-carrying conductor.

2.Calculate the magnetic flux through a rectangular loop with dimensions a = 4cm, b = 5cm in a magnetic field with induction B = 1.1T, if the plane of the loop forms an angle β = 300 with the direction of induction.
Solution:
Analysis:
S = a·b = 4cm·5cm = 20cm2 = 20·10–4m2, B = 1.1T, α = 900 - β = 600
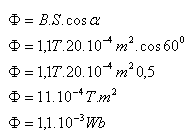
The magnetic flux through the rectangular loop is φ = 1.1·10–3Wb.
3.What is the magnetic induction B if a circular area with radius r = 5cm is penetrated by a magnetic flux of 4·10–2Wb? The area is perpendicular to the field lines. (β = 900)
Solution:
Analysis:
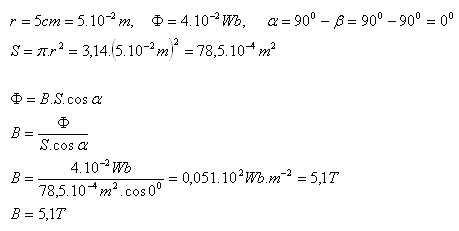
The magnetic induction is B = 5.1T.
4.What is the radius of a circular coil whose axis forms an angle α = 300 with B = 5.89T, if a magnetic flux of 4·10–2Wb passes through the coil?
Please log in to view the solution.
5.In which case will the induced voltage in a conducting loop be greater? If the magnetic flux decreases from 1Wb to zero in 0.5s, or if it increases from zero to 1Wb in 0.1s? What will be the polarity of the induced voltage?
Please log in to view the solution.
6.A horizontal conductor 2m long was released at time 0s and fell freely in a plane perpendicular to the north-south direction (B = 5·10–5T, β = 900). Determine the induced voltage at the ends of the conductor at time 5 seconds.
Please log in to view the solution.
7.Determine the self-inductance of a loop if a change in current of ΔI = 0.1A produces a magnetic flux Φ = 4·10-5Wb through the loop’s cross-section.
Please log in to view the solution.
8.How many turns does a coil of length 30cm have if a current I = 0.5A produces a magnetic field of intensity 833A·m-1 inside the coil?
Please log in to view the solution.
9.How many turns must a cylindrical coil have in order to induce an average voltage of 10V, if the magnetic flux in its core changes from 0.024Wb to 0.056Wb in 0.32 seconds?
Please log in to view the solution.
10.Calculate the self-inductance of an air-core coil with 1000 turns, length 20cm, and diameter 2.0cm. What is the energy of the magnetic field if the coil carries a current of 2.5A?
Please log in to view the solution.
11. In a homogeneous magnetic field with magnetic induction B = 30 T, a straight conductor with length l = 1.5 m moves perpendicular to the induction lines with velocity v = 0.5 m·s-1. Determine the induced voltage at the end of the conductor.
Please log in to view the solution.12.What was the change of electric current in a coil with inductance L = 1.4 H, if during the time interval Δt = 10-2 s an induced voltage Ue = -70 V occurs?
Please log in to view the solution.13.A cylindrical coil with 100 turns carries a current of 12 A. The magnetic flux in the cavity of the coil is 5.2 mWb. Calculate the energy of the magnetic field of the coil.
Please log in to view the solution.14.The magnetic field of a coil through which a current I = 6.2 A flows has energy Em = 0.32 J. Calculate the inductance of the coil.
Please log in to view the solution.15.The magnetic flux of a horseshoe magnet is Φ = 20·10–5 Wb. Determine the magnetic induction at the poles whose cross-sectional area is S = 5 cm2.
Please log in to view the solution.16.A cylindrical coil of wire with total resistance 160 Ω has 1000 turns and a cross-sectional area of 40 cm2. The coil is placed in a homogeneous magnetic field such that its axis is parallel to the induction lines. The magnitude of the magnetic field changes uniformly with time such that ΔB = 10-3 T·s-1 Δt. Determine the heat produced in the coil over 30 seconds.
Please log in to view the solution.17.Two parallel conductors are placed in a horizontal plane at a mutual distance l = 1 cm. A bulb with resistance R = 5 Ω is connected between the ends of the conductors. A third conductor, placed perpendicular to the given conductors, can slide along distance x with negligible friction. The homogeneous magnetic field has magnetic induction B = 10-3 T. Determine the magnitude of the force that must be applied to move the conductor at constant velocity v = 10 cm·s-1.
Please log in to view the solution.18.Calculate the magnetic flux Φ in the cross-section of the cavity of an air-filled cylindrical coil. The coil has length l = 1.6 m, radius r = 4.8 cm, 1400 turns, and carries current I = 6.3 A.
Please log in to view the solution.19.A beam of ions of a silicon isotope with mass number 28 and electric charge Q = 1.602·10-19 C moves in a homogeneous magnetic field B = 0.18 T in a vacuum along a circular path with radius r = 21 cm. Calculate the kinetic energy of the ion.
Please log in to view the solution.20.Express the units of the physical quantities Q, B, Φ, L, U, R, W, P as a product of basic SI units (kg, m, s, A).
Please log in to view the solution.