The surface of the liquid
1. Explain the physical concepts of “surface layer” and “capillarity”
Solution:
The surface and a drop of liquid, or a bubble, behave as if there were an elastic film on their surface – the “surface layer.” It has a thickness of about 10-9 m. It is formed by a layer of molecules. The surface and drop have one surface, a bubble has two surfaces.
Surface tension:
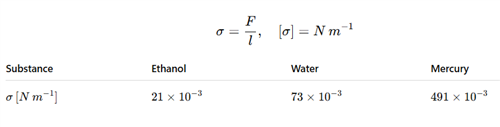
Surface tension coefficients:
| Substance | |
|---|---|
| Alcohol | |
| Water | |
| Mercury |
For: Surface, Droplet vs. Bubble, Membrane
| Quantity | Surface, Droplet | Bubble, Membrane |
|---|---|---|
| Surface force | ||
| Surface energy | ||
| Capillary pressure | ||
| Hydrostatic pressure |
l = 2π.r S = π.r2
- Capillary elevation = rise of a wetting liquid in a capillary
- Capillary depression = lowering of a non-wetting liquid in a capillary
2.What is the mass of a water drop (σ = 73.10-3 N.m-1) that dripped from a tube with a radius of 0.5 mm?
Solution:
Analysis:
R = 0.5·10-3 m, g = 10 m.s-2, σ = 73.10-3 N.m-1
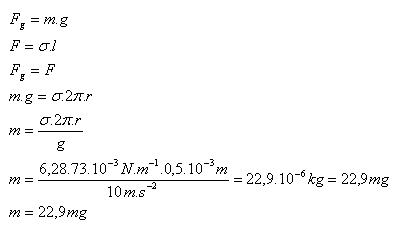
The mass of the water drop is m = 22.9 mg.
3.A capillary measured 100 drops of ethanol with a mass of 1.81 g. The same number of water drops from the same capillary and at the same temperature has a mass of 6.26 g. Determine the surface tension of ethanol σ1 if the surface tension of water is σ2(H2O) = 73.10-3 N.m-1.
Solution:
Analysis:
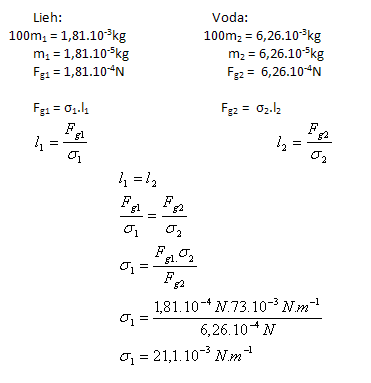
The surface tension of ethanol is σ1 = 21.1·10-3 N.m-1
4.Water drips from a capillary with radius r = 0.9 mm. How many drops of water are in 1 cm3 of water? (σ = 73.10-3 N.m-1, ρ = 103 kg.m-3)
Please log in to view the solution.
5.A movable rod with a length of 40 mm on a frame with a soap film is in equilibrium when loaded with a weight of 320 milligrams. What is the surface tension of the soap solution in water in contact with air? The film has two surfaces. (Neglect the mass of the rod)
Please log in to view the solution.
6. Determine the work (in an isothermal process) required to inflate a soap bubble with a diameter of 14 cm. The bubble has two surfaces. σ = 40·10-3 N.m-1
Please log in to view the solution.
7.A soap bubble (σ = 40·10-3 N.m-1) has a radius of 2 cm. What work is done if we increase its radius by 1 cm?
Please log in to view the solution.
8. Capillary rise – elevation – of ethanol in a narrow capillary is 12 mm. What is the inner diameter of the capillary? (ρ = 800 kg.m-3, σ = 21.4 mN.m-1)
Please log in to view the solution.
9.The capillary has an inner diameter of 0.2 mm. Calculate:
- a.) How high will benzene rise in the capillary (ρ = 870 kg.m-3, σ = 29,1.10-3N.m-1)
- b.) How does the rise height of benzene change if we use a capillary with double the radius
- c.) How would the result of the experiment change on the Moon. (gM = 0.167g)
10. What will be the difference in levels in two capillaries immersed in a liquid (ρ = 800 kg.m-3, σ = 22.10-3N.m-1)? The capillaries have different inner diameters: d1 = 0.4mm, d2 = 1mm
Please log in to view the solution.
11.On a frame with a movable partition of length 10 cm there is a soap film. What work must be done to move the partition by 2 cm?
Please log in to view the solution.12.A small frame with a movable arm of mass 1.2 g is in a vertical position. The weight force keeps the arm and the film in equilibrium. What is the length of the arm if the surface tension of the film is 60.10-3N.m-1? How does the surface energy of the film change if the arm is moved by 2 cm?
Please log in to view the solution.13.A water droplet with a radius of 3 mm is sprayed into tiny droplets with a radius of 3.10-5 mm. By how many times does the surface energy of the water droplets increase in the process?
Please log in to view the solution.14.What is the pressure of the air in a soap bubble with a radius of 2 mm if the atmospheric pressure is 101325 Pa?
Please log in to view the solution.15.In a capillary, kerosene rose to a height of 13 mm and in another capillary with the same radius mercury fell by 13.9 mm. What is the surface tension of mercury, if the density of mercury is 13.6.103 kg.m3? The surface tension of kerosene is 27.10-3N.m-1 and its density is 0.8.103 kg.m-3.
Please log in to view the solution.16. In a capillary with a diameter of 2 mm there is water. How tall a column of water will remain in the capillary if both ends remain open?
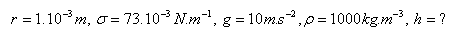
17.From a capillary, 100 drops of water with a total mass of 2.4 g dripped. The mass of 50 drops of glycerine from the same capillary is 1.1 g. What is the ratio of the surface tensions of the two liquids?
Please log in to view the solution.18. What is the surface tension of glycerine? (Use the result of problem 17)
Please log in to view the solution.19.When N water droplets with a radius of 2.10–6 m merge into one droplet with a radius of 2.10–3 m, 3.668 mJ of energy is released. By how much does the water heat up?
Please log in to view the solution.20.Calculate the surface energy of a mercury droplet that has a volume of 1 cm3.
Please log in to view the solution.