Photometry
1. Ktoré sú dôležité pojmy fotometrie?
Riešenie:

2.
Definujte:
Riešenie:
- Jedna kandela (cd) je 1/600 000 z m2 povrchu absolútne čierneho telesa pri teplote tuhnutia platiny (17730C) za normálneho tlaku (101325 Pa) Absolútne čierne teleso je fiktívne teleso, ktoré by všetko dopadajúce žiarenie pohlcovalo.
- Jeden lumen (lm) je svetelný tok, ktorý vyžaruje bodový zdroj o svietivosti jednej kandely do priestorového uhla jedného steradiána.
- Plocha má osvetlenie jeden lux (lx), ak na 1m2 tejto plochy dopadá svetelný tok jeden lumen.
3. Ľudské oko vníma svetelný vnem pri minimálnom osvetlení sietnice E=2.10-9lx. Z akej maximálnej vzdialenosti za ideálnych podmienok (absolútna tma) môžeme pozorovať plameň sviečky so svietivosťou I = 1 cd.
Riešenie:
Rozbor:
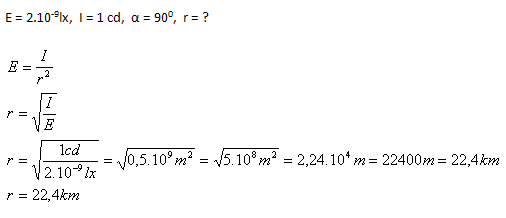
Plameň sviečky môžeme pozorovať z maximálnej vzdialenosti 22,4 km.
4.
Fotometer je osvetlený z jednej strany žiarovkou I1 = 50cd, ktorá je od fotometra vzdialená r1=0,6m. Na druhej strane je vo vzdialenosti r2 = 0,96m žiarovka neznámej svietivosti (I2 = ?). Aká je jej svietivosť, ak je fotometer z obidvoch strán rovnako osvetlený?
Riešenie:
Rozbor:
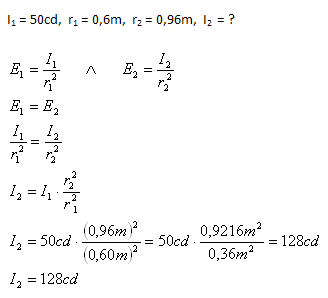
Svietivosť druhej žiarovky je I2 = 128cd.
5.
Nad stolom kruhovej platne s polomerom r = 0,8m visí vo výške h1 = 2m žiarovka svietivosti I = 50cd. Určite osvetlenie
- a) stredu platne
- b) okraju platne
Riešenie:
Rozbor:
I = 50cd, r = 0,8m, h1 = 2m, h2 = ? = vzdialenosť žiarovky od okraju platne. Veličiny r, h1, h2 tvoria pravouhlý trojuholník s preponou h2. Uhol α je ostrý uhol proti odvesne r.

Osvetlenie stredu platne je 12,5 luxov, okraju platne 10 luxov.
6.
Dve žiarovky so svietivosťou I1 = 80cd a I2 = 200cd sú umiestnené vo výške h = 2,5m nad vodorovnou doskou stola. Ich vzájomná vzdialenosť je d = 3m. Aké je osvetlenie stola v mieste, kde dopadajú lúče z prvej žiarovky?
Riešenie:
Rozbor:
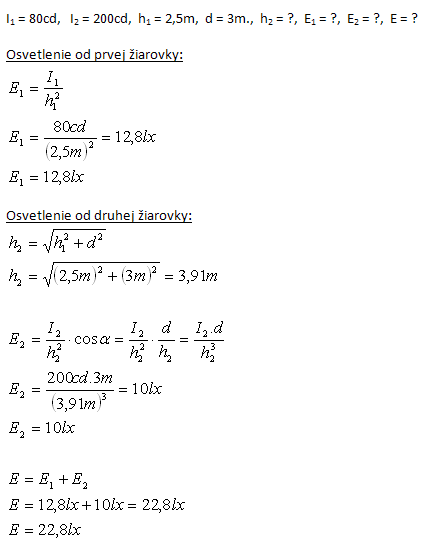
Výsledné osvetlenie od obidvoch žiaroviek je E = 22,8 luxov.
7. Osvetlenie vodorovného povrchu Zeme pri výške Slnka nad horizontom 450 je E1 = 80 000lx. Určite osvetlenie povrchu Zeme pri výške Slnka nad horizontom 250.
Riešenie:
Rozbor:
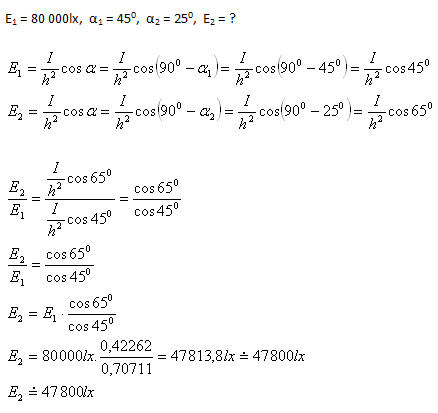
Osvetlenie povrchu Zeme pri výške Slnka nad horizontom 250 je 47800 luxov.
8. Stena je osvetlená dvoma rovnakými sviečkami postavenými tesne vedľa seba vo vzdialenosti 0,8m od steny. O akú vzdialenosť x treba priblížiť k stene sviečku, ak jedna zhasla (I2 = 0) , aby stena bola rovnako osvetlená ako predtým?
Riešenie:
Rozbor:
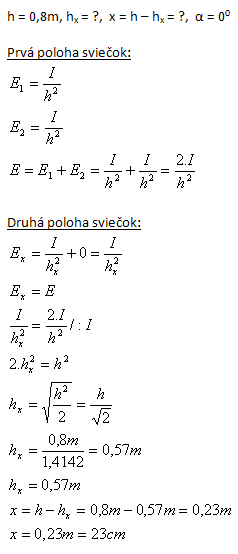
Sviečku treba k stene priblížiť o 23 cm.
9.
Kruhová plocha s polomerom r = 3m je osvetlená reflektorom zo vzdialenosti h = 60m. Osvetlenie plochy je E = 4 lx. Vypočítajte:
- a) svietivosť zdroja
- b) svetelný tok dopadajúci na plochu
Riešenie:
Rozbor:
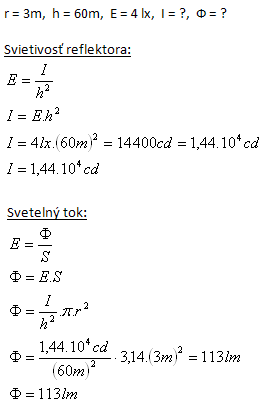
Svietivosť reflektora je I = 1,44 cd, svetelný tok Ф = 113 lm.
10. Dva svetelné zdroje so svietivosťou I1 = 25cd a I2 = 49cd sú umiestnené vo vzdialenosti d = 1m. V ktorom mieste ich spojnice musí byť postavené tienidlo, aby bolo osvetlené rovnako obidvoma zdrojmi? (I2 je na ľavo od I1)
Riešenie:
Rozbor:
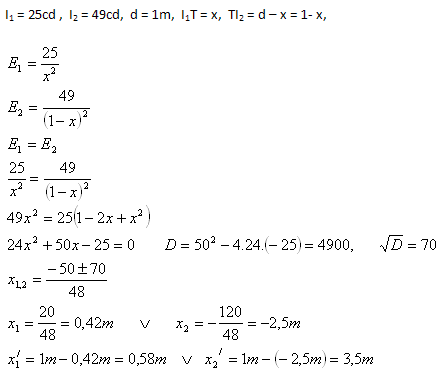
Pre postavenie tienidla sú dve možnosti:
- 0,42m od I1 a 0,48m od I2 ,
- -2,5m od I1 (vpravo od I2) a 3,5m od I2.