Ideal gas
1. Explain the properties of an ideal gas
Solution:
An ideal gas is not a real gas; it is a model of a gas. Its molecules have negligible size and identical masses m0. Collisions between molecules and their impacts on the container walls are perfectly elastic. Impacts of molecules on the container walls are the cause of the gas pressure. Molecules do not exert forces on each other. Under "standard conditions" (p0 = 101325 Pa, T0 = 273.15 K) the properties of real gases approach those of an ideal gas. Under these conditions 1 mol of any gas always has volume V0 = 22.415×10-3 m3·mol-1.

2.Calculate the root-mean-square speed of an oxygen molecule O2 at temperature 0°C!
Solution:
Analysis:
T = t + 273.15
T = 0 + 273.15 = 273.15
m0 = Ar·mu = 2·16.00·1.66·10-27 = 53.12×10-27 kg
k = 1.38×10-23 J·K-1
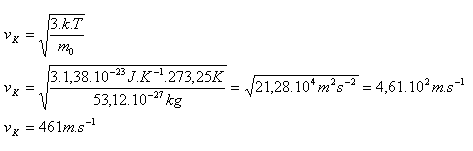
The root-mean-square speed of an O2 molecule is vK = 461 m·s-1
3.Determine the ratio of the root-mean-square speeds of hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) molecules at the same temperature.
Solution:
Analysis:
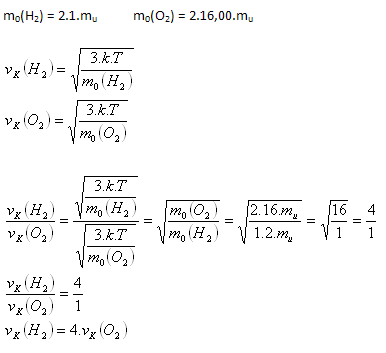
Hydrogen molecules will move 4 times faster than oxygen molecules.
4.What is the air pressure at temperature T = 273.15 K, if the mass of an air molecule is m0 = 47.45×10-27 kg and the air density at this temperature is ρ = 1.27584 kg·m-3.
Please log in to view the solution.
5.An ideal gas with mass m = 3.8×10-2 kg is enclosed in a vessel with volume 10 liters and has pressure p = 0.49 MPa. Determine the root-mean-square speed of the gas molecules.
Please log in to view the solution.
6.Calculate at what temperature the root-mean-square speed of helium is 1300 m.s-1, vk = 1300 m.s-1, Ar(He) = 4.003, NA = 6.022·1023 mol-1, k = 1.38·10-23 JK-1
Please log in to view the solution.
7.How does the mean kinetic energy that a molecule of an ideal gas has due to random motion change if the thermodynamic temperature is increased 3 times?
Please log in to view the solution.
8.Determine the change in internal energy of an ideal gas with monoatomic molecules if its temperature increases from 200 K to 400 K. The gas contains 1028 molecules.
Please log in to view the solution.9.How does the pressure of an ideal gas change if the number density of molecules of this gas NV increases 4 times and the root-mean-square speed vK does not change?
Please log in to view the solution.
10.What is the pressure of oxygen O2 with density 1.41 kg.m-3 at a temperature of 00C if its root-mean-square speed is vK = 461 m.s-1?
Please log in to view the solution.
11.An ideal gas with mass 6 kg is enclosed in a vessel with volume 5 m3 at a pressure of 2·105 Pa. Determine the root-mean-square speed of the gas molecules.
Please log in to view the solution.
12.An argon atom moving with speed 500 m.s-1 is elastically reflected from the wall of a vessel. The velocity vector of the argon atom makes with the normal to the wall an angle a.) 00, b.) 600. Determine in both cases the magnitude of the change of its momentum after a perfectly elastic reflection from the wall of the vessel.
Please log in to view the solution.13.The root-mean-square speed of chlorine Cl2 molecules at 00C is 310 m.s-1. Calculate the density of chlorine at a pressure of 105 Pa.
Please log in to view the solution.
14. What is the mean kinetic energy of a molecule of an ideal gas at a temperature of -1000C?
Please log in to view the solution.