Electric current in gases and vacuum
1.How does electric current arise in gases and in a vacuum?
Solution:
Electric current in gases (a discharge) is the ordered motion of free ions and electrons. Only an ionized gas conducts electric current. Ionization energy is the smallest possible energy needed to ionize a gas (to break a neutral atom into ions and electrons).
Ionization energy:
| Mercury | 10,4eV |
| Hydrogen | 13,6eV |
| Oxygen | 13,6eV |
| Nitrogen | 14,5eV |
| Neon | 21,6eV |
m = mass of the particle,
v = speed of the particle,
Q = charge of the particle,
λ = mean free path of the particle,
E = magnitude of the electric field intensity,
U = voltage between the electrodes
Electric current in a vacuum—cathode rays—is a directed flow of electrons emitted perpendicularly from the cathode.
- Photoemission of electrons = emission caused by intense light
- Thermoemission of electrons = emission caused by high temperature
- Work function = the smallest energy needed to release an electron from a body
| Cesium | 1.93 eV | Iron | 4.77 eV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesium | 3.69 eV | Nickel | 5.00 eV |
| Tungsten | 4.15 eV | Platinum | 5.36 eV |
2.Between the plates of a capacitor with an air dielectric, which are 0.5 cm apart, the electric voltage is 10 kV. What is the speed of an electron at the moment of collision with an oxygen molecule that it ionized? What is the mean free path of the electron?
Solution:
Analysis:
l = 5.10–3m, U = 104V, Ei = 13,6eV = 13,6.1,602.10–19J = 21,787.10–19J, Q = e =1,602.10–19C,
me = 9,1.10–31kg,
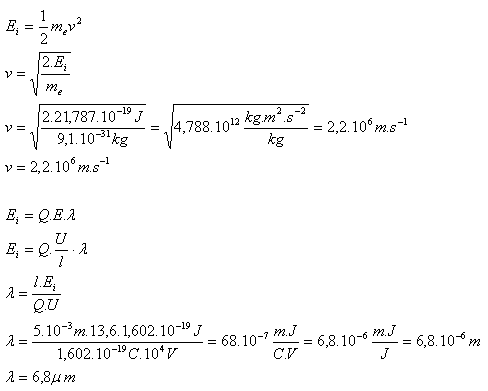
- The electron at the moment of collision with an oxygen molecule had a speed v = 2,2.106m.s–1
- The mean free path of the electron is 6,8μm.
3.At what voltage does a neon lamp light up if the ionization energy is 21,6eV and the mean free path of electrons is 1 mm? The distance between the lamp’s electrodes is 1 cm.
Solution:
Analysis:
Ei(Ne) = 21,6eV = 34,6.10-19J, λ = 10–3m, l = 10–2m, Q = e = 1,602.10-19C, U = ?
Ei = Q.E.λ
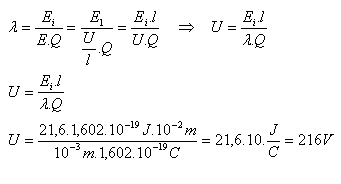
The neon lamp lights up at a voltage U = 216V.
4.The voltage between the anode and cathode, which are 10 cm apart, is 300 V. Determine the magnitude of the electron speed upon impact on the anode, their acceleration, and the time of travel from the cathode to the anode.
Please log in to view the solution.
5.Determine how many times the electron speed upon impact on the anode at voltage U1=360V is greater than at voltage U2=40V.
Please log in to view the solution.
6.An electron entered the horizontal deflection plates of a television screen. Assuming a homogeneous electric field between them with intensity 105V.m–1 and neglecting the effect of the gravitational field, determine the acceleration of the electron in the electric field!
Please log in to view the solution.
7.If the magnitude of the electric field intensity is 3.106V.m–1, a spark discharge occurs in air at normal pressure. Calculate the kinetic energy of an electron that it attains if its mean free path is 5.10–6m.
Please log in to view the solution.
8.At a voltage of 800 V, a current of 5 mA arises in a cathode tube. How much heat is released at the anode in 1 minute, assuming that all kinetic energy is converted into heat?
Please log in to view the solution.
9.An electron that moved in an electric field from point A to point B increased its speed from 800 km.s–1 to 4000 km.s–1. Determine the voltage between these points!
Please log in to view the solution.
10.A discharge in the form of lightning occurred between the ground and a cloud, transferring a charge of 20 C. The potential difference between the cloud and the ground was 106V. The lightning lasted 10–3s. Determine the energy of the discharge and the current.
Please log in to view the solution.
11.Hydrogen vapor is ionized by β radiation (electrons). What minimum speed must the ionizing electrons have for ionization to occur?
12.What is the mean free path of an electron if the electric field intensity in which mercury vapor is located is
E = 104 V·m-1. The ionization energy of mercury is Ei = 10.4eV.
13.Given is the table:
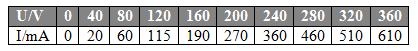
Determine how many times greater the velocity of electrons impacting the electrode at current I1 = 610mA is compared to current I2 = 115mA. Values in the table.
14.What speed does an electron obtain when striking the anode of an evacuated tube, if U = 3000V and the initial speed is v0 = 0?
Please log in to view the solution.15.A flame creates on average 3×1011 pairs of electrons and singly charged ions per second between the plates of an air capacitor. Determine the value of the saturation current flowing between the plates.
Please log in to view the solution.16.A metal sphere with radius r = 3cm is placed in air. To what potential can the sphere be charged if the electric field intensity at which spontaneous discharge occurs in air has a magnitude of 3MV·m-1?
Please log in to view the solution.17.What is the ionization energy of neon if the electric field intensity is E = 4.32×106 V·m-1 and the free path of the electron is λ = 5×10-6 m?
Please log in to view the solution.18.Determine the electric field intensity E needed for ionization of an electron by collision in air (Ei = 15eV) at normal pressure. The free path of the electron is λ = 3×10-6 m.
Please log in to view the solution.19.An electron entered with speed v = 6×107 m·s–1 between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor in a horizontal position. The distance between the plates is d = 1cm. The voltage between the plates is U = 600V. Determine the acceleration of the electron.
Please log in to view the solution.20.Calculate the deflection (y) of the electron at the end of the capacitor, which has a length l = 5cm. Additional data and values are in example no. 19.
Please log in to view the solution.