Optical instruments
1. Which optical instruments do you know?
Solution:
Optical instruments are devices for observing small or distant objects. They enlarge the visual angle of the object. It is the angle of the rays that pass through the edge points of the object and enter the eye.
Among optical instruments belong:
a) the eye,
b) magnifying glass,
c) microscope,
d) telescope,
e) camera, projector, etc.
The eye is a compound optical system. It creates a real, diminished, and inverted image on the retina (yellow spot).
Near point = 0.1 m
Conventional viewing distance = 0.25 m
Healthy eye:
Φ0=0.11=10dpt
Eye with glasses:
Φ=d1−a1
Φ0,Φ= optical power, d=0.25m,a= distance of the object from the eye between the image (yellow spot) and the eye lens.
A magnifying glass is any converging lens for which: f<d.
Angular magnification of a magnifying glass:
γ=tanτtanτ′=fy′⋅yd=fd
A microscope is an optical instrument for enlarging the visual angle when observing very small objects. Its main parts are the objective and the eyepiece.
The objective (f1) and the eyepiece (f2) are converging lenses. It is a compound optical microscope. The distance between the objective and the eyepiece is the tube length.
Tube length l=f1+Δ+f2.
Angular magnification of a microscope:
γ=yy′⋅f2d=f1Δ⋅f2d=Z1Z2
A telescope (Kepler’s, Galileo’s) is an optical instrument for enlarging the visual angle when observing distant objects.
The objective (f1) and the eyepiece (f2) are converging lenses.
Δ=0,l=f1+f2.
Angular magnification of a telescope:
2. Under what visual angle do we observe from Earth the Moon (RM=1738 km, lM=384 493km ) and the Sun (RS=695 980 km, lS=149 597 892 km )? τ = the visual angle under which we observe the radius of the Moon or the radius of the Sun.
Solution:

We observe the Moon under an angle of 31‘, and the Sun under an angle of 32‘.
3. Up to what distance can the human eye distinguish two points that are 1m apart?
Solution:
Analysis:
y = 1m, the eye can distinguish two points if τ is at least 1‘, x = ?
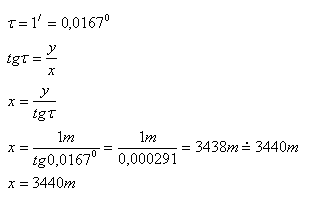
The human eye can distinguish two points up to a distance of x = 3440m
4. What is the maximum and minimum focal length of a lens that can be used as a magnifying glass? With a magnifying glass, angular magnification can be achieved.
Solution:
Analysis:
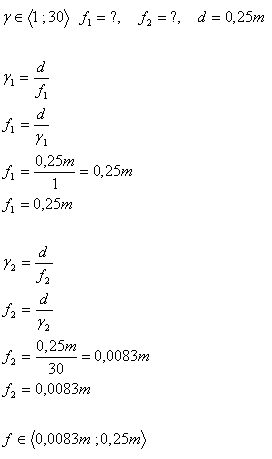
The maximum focal length of the magnifying glass is 0.25m, the minimum is 0.0083m.
5. A farsighted eye has the nearest clear vision distance at 2m. What glasses are needed?
Solution:
Analysis:
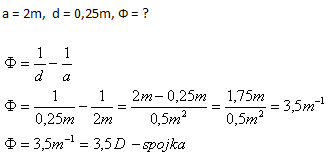
A farsighted eye needs a converging lens with optical power Ф = 3.5 D.
6. Determine the magnification of a microscope with an objective focal length of 4mm, an eyepiece of 4cm, and an optical interval of 16cm.
Solution:
Analysis:
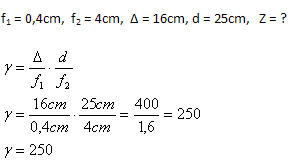
The microscope magnifies 250 times.
7. A microscope has magnification γ = 320 and an objective focal length of 5mm and an eyepiece of 2.5cm. Determine the distance between the objective and the eyepiece l and the tube length L.
Solution:
Analysis:
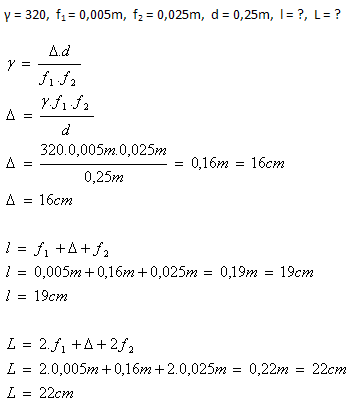
The distance between the objective and the eyepiece is l = 19cm. The tube length is L = 22cm.
8. What lenses are needed to construct a Keplerian telescope if the objective and the eyepiece are 80cm apart and the telescope magnifies 19 times?
Solution:
Analysis:
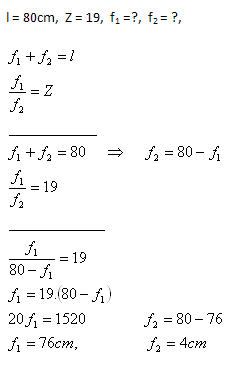
The Keplerian telescope has an objective converging lens with f1 = 76cm and an eyepiece with f2 = 4cm.
9. The distance between the objective and the eyepiece of a Galilean telescope is 38cm. The magnification of the telescope is 20. Determine the focal length of the objective and the eyepiece.
Solution:
Analysis:
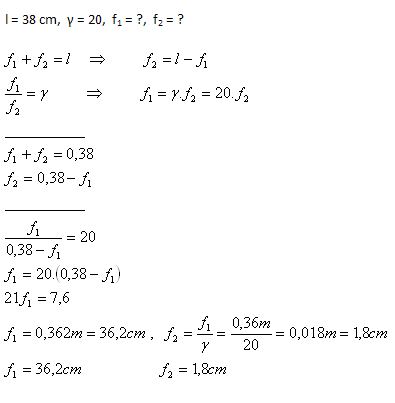
The focal length of the objective is f1 = 36.2cm, and of the eyepiece f2 = 1.8cm.
10. In a telescope with an objective focal length f1 = 100cm and an eyepiece f2 = 10cm we observe a tower 40m high. Its image in the telescope has a height of 4cm. How far away is the tower? (d = 25cm).
Solution:
Analysis:
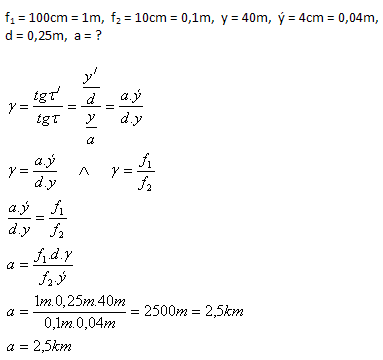
The tower is 2.5km away from the telescope.