Substance characteristics
1.
Which physical quantities characterize a substance?
Solution:

2.
Determine the rest masses of atoms of the elements H, C, Zn. What is the relative mass of Uranium if its rest mass is ma(U) = 3.95·10-25 kg. Use the tables.
Solution:
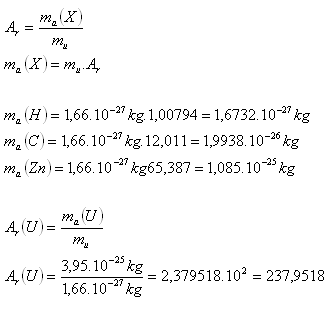
The relative mass of Uranium is approximately Ar(U) = 238
3.
Estimate the approximate number of atoms contained in an iron weight with mass 1 kg. How long would a line be if all these atoms were arranged tightly next to each other in a single straight line? The diameter of an atom is about 10-10 m.
Solution:
Analysis:
m = 1 kg, d = 10-10 m, mu = 1.66·10-27 kg, Ar(Fe) = 55.847
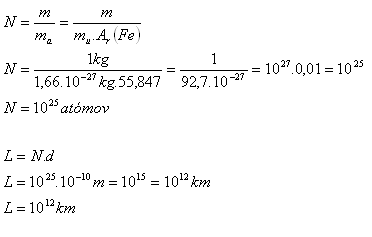
In one kilogram of iron there are 1025 atoms. The length of the line formed by these atoms would be 1012 km. This is about 6600 times greater than the distance Earth – Sun.
4. Determine the number of electrons contained in 1 g of copper. What is their total mass if the mass of a single electron is 9.1·10-31 kg?
Solution:
Analysis:
m = 1 g = 10-3 kg, me = 9.1·10-31 kg, mu = 1.66·10-27 kg, Ar(29Cu) = 63.546
Rest mass of a Cu atom:
ma(Cu) = mu·Ar(Cu)
ma(Cu) = 1.66·10-27 kg · 63.546 = 105.486·10-27 kg
Number of atoms:
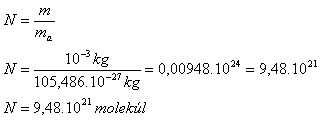
Number of electrons:
29Cu – each atom has 29 electrons
N‘ = 29·N = 29·9.48·1021 = 2.75·1023
Total mass of all electrons:
m = N‘·me = 2.75·1023 · 9.1·10-31 kg = 25·10-8 kg
In one gram of copper there are 2.75·1023 electrons, which have a mass of 25·10-8 kg.
5.
Find out whether a molecule of nitric acid HNO3 has a greater mass than a molecule of silver oxide Ag2O. Use tables.
Solution:
HNO3
Ar(H) = 1.008
Ar(N) = 14.010
3·Ar(O) = 48.000
Ar(HNO3) = 63.018 m(HNO3) = 63.018·1.66·10-27 kg
m(HNO3) = 1.46·10-25 kg
Ag2O
2·Ar(Ag) = 215.74
Ar(O) = 16.00
Ar(Ag2O) = 231.74 m(Ag2O) = 231.74·1.66·10-27 kg
m(Ag2O) = 3.8469·10-25 kg
m(Ag2O) > m(HNO3)
Assumption is not valid.
6.
Calculate the amount of substance corresponding to 4.82·1024 hydrogen atoms.
Solution:
Analysis:
N = 4.82·1024 hydrogen atoms, NA = 6.022·1023 mol-1
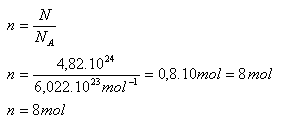
The given number of hydrogen atoms corresponds to n = 8 moles.
7.
Determine the amount of substance of water with volume 3.6 L.
Solution:
Analysis:
V = 3.6 L, m = 3.6 kg,
2·Ar(H) = 2.016
Ar(O) = 16.000
Ar(H2O) = 18.016
Mm = 18.016·10-3 kg·mol-1
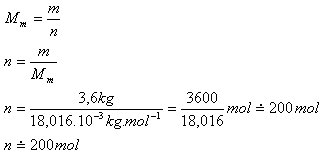
The volume 3.6 liters of water is 200 moles.
8.
Find out whether water with amount of substance 1 mol can be poured into a cylinder with volume 10 cm3.
Solution:
Analysis:
n = 1 mol, V = 10 cm3, Mm = 18.016·10-3 kg (see example 7), ρ = 103 kg·m-3
Volume of one mole of water:
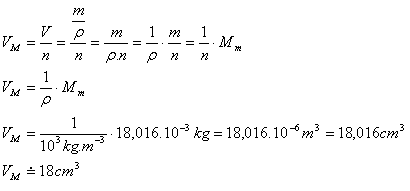
Volume of the cylinder VV = 10 cm3
VM > VV
Water cannot be poured into the cylinder because the volume of one mole of water is 18 cm3 and the container only has 10 cm3.
9. A room has dimensions a = 4 m, b = 4 m, c = 3 m. How many molecules of air are in it? (Mm = 29·10-3 kg·mol-1, ρ = 1.276 kg·m-3)
Solution:
Analysis:
V = a·b·c
V = 4 m · 4 m · 3 m = 48 m3,
Mm = 29·10-3 kg·mol-1, ρ = 1.276 kg·m-3
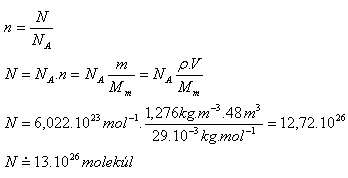
There are approximately 1.3·1027 molecules in the room.
10. From the surface of a water droplet with volume 1 mm3, water containing about 106 molecules evaporates in 1 second. In what time will the entire droplet evaporate?
Solution:
Analysis:
V = 1 mm3 = 10-9 m3, N‘ = 1016 s-1, Mm(H2O) = 18.016·10-3 kg·mol-1
ρ = 1000 kg·m-3, NA = 6.022·1023 mol-1
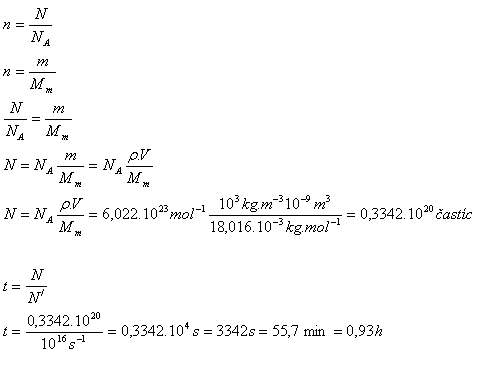
The whole droplet will evaporate in just under 1 hour.