Work in an electric field
1. Characterize the physical quantities: work in an electric field, electric potential and electric voltage.
Solution:

2.What amount of work does an electric field of intensity 104N.C-1 perform when it moves a charge of 20 μC along the field line for a distance of 10 cm.
Solution:
Analysis:
E = 104N.C-1, Q0 = 20 μC = 20.10-6C, d = 10 cm = 10-1m
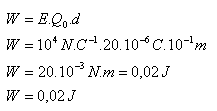
The electric field does work W = 0,02 J
3.What is the potential of a conductor if transferring a charge of 50 μC from a point of zero potential to its surface required work of 0.2 J?
Solution:
Analysis:
Q0 = 50.10-6C, W = 2.10-1J, φ = ?
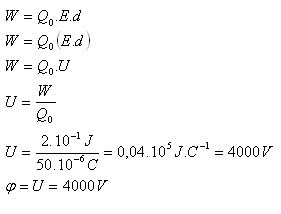
The conductor has potential φ = 4000 V.
4.In a homogeneous electric field with intensity 1 kV.m-1, a particle with charge 25.10-9C moves along a path of 2 m.
- a) What work do the forces of the electric field perform when moving the particle?
- b) What is the electric voltage between the starting and ending points of the displacement?
Solution:
Analysis:
E = 103 V.m-1, Q0 = 25.10-9C, d = 2 m , W = ? U = ?
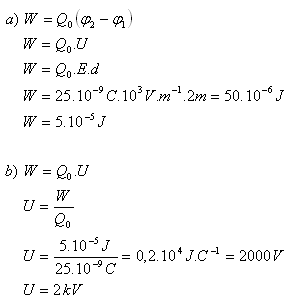
- The field forces perform work W = 5.10-5J.
- The voltage between the starting and ending points of the displacement is U = 2 kV.
5.What speed will an electron (Qe= 1,602.10-19C, me = 9,1.10-31kg) reach when passing through a potential difference of 100 V?
Solution:
Analysis:
Qe= 1,602.10-19C, me = 9,1.10-31kg, Δφ = U = 100 V = 102V
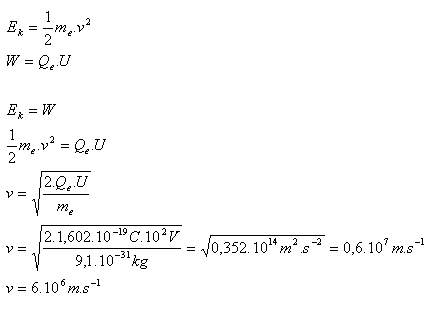
The electron reaches speed v = 6.106m.s-1.
6.Determine the intensity of the electric field between two parallel conducting plates separated by 5 cm if the voltage between them is 150 V. What work do the field forces perform when transferring a charge of 1 μC from one plate to the other?
Solution:
Analysis:
d = 5cm = 5.10-2m, U = 150V, Q0 = 1μC = 10-6C, E = ?, W = ?
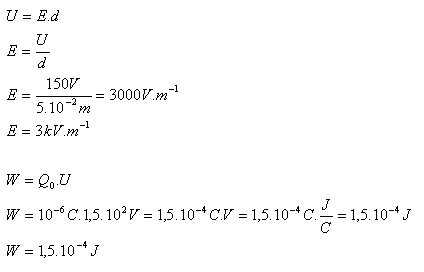
The electric field intensity between the two parallel conducting plates is E = 3 kV.m-1. The field forces perform work W = 1,5.10-4J.
7.An alpha particle ( mα = 6,7.10-27kg, Q0α = 3,2.10-19C) entered a homogeneous electric field with velocity 2.106m.s-1. The particle stopped after travelling 2 m.
- What potential difference did the particle traverse?
- What is the magnitude of the electric field intensity?
Solution:
Analysis:
mα = 6,7.10-27kg, Q0α = 3,2.10-19C, v = 2.106m.s-1, d = 2m, U = ?, E = ?
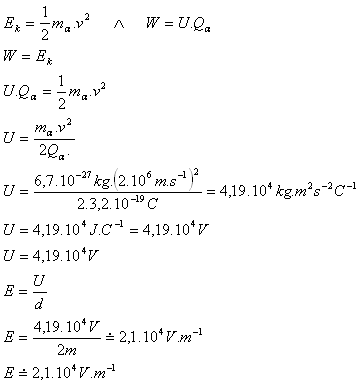
- The particle traversed potential difference Δφ = U = 4,19.104V.
- The electric field intensity is E = 2,1.104V.m-1.
8.What electric charge does a microscopic oil droplet of mass 6,4.10-16kg have if it hovers between the plates of a charged capacitor? The capacitor plates are 1 cm apart and the voltage between them is 400 V. (Experiment R.A. Millikan)
Solution:
Analysis:
m = 6,4.10-16kg, d = 1cm = 10-2m, U = 4.102V, g = 10m.s-2, Q = ?
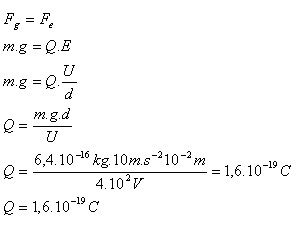
The electric charge of the oil droplet is the elementary charge Q = 1,6.10-19C.
9.What work do the forces of the electric field created by charge Q = 2 μC perform when moving charge Q0 = 1 nC from a point 10 cm from charge Q to a point 20 cm from charge Q.
Solution:
Analysis:
Q = 2μC = 2.10-6C, Q0 = 1 nC = 10.10-9C, r1 = 0,1m, r2 = 0,2m, k = 9.109N.m2.C-2
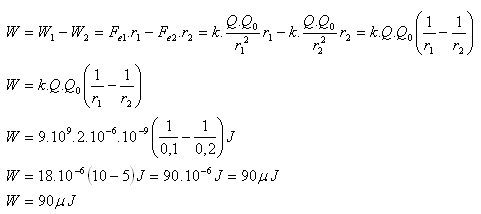
The electric field forces perform work W = 90 μJ.
10.An electron (e = 1,602.10-19C) moves in a homogeneous electric field from a potential level of 200 V to a level of 300 V. The initial speed is zero, the final speed is 5,93.106m.s-1. Determine:
- the increase in the electron's energy as it passes between the two potential levels
- the mass of the electron
Solution:
Analysis:
e = 1,602.10-19C, U = Δφ = 100V, v0 = 0, v = 5,93.106m.s-1
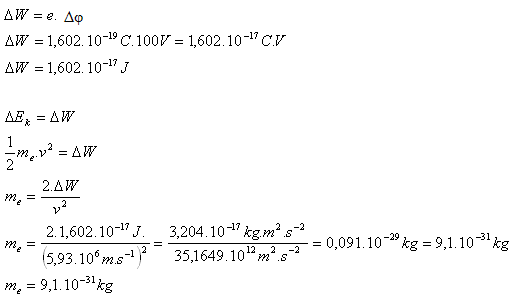
- The increase in the electron's energy is ΔW = 1,602.10-17J.
- The mass of the electron is me = 9,1.10-31kg.