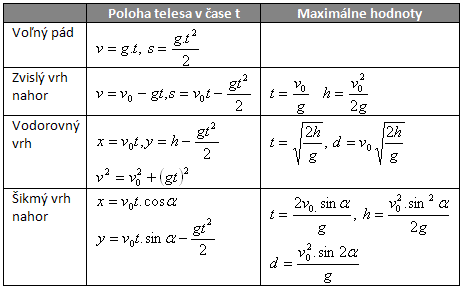
Motions in a uniform gravitational field
1.Characterize motions in the Earth's uniform gravitational field.
Solution:
The gravitational field extending to a small height above the Earth's surface (h << RZ) can be considered uniform. Such a field has the same values of physical characteristics at every point in space. Besides free fall, this includes vertical upward throw, horizontal throw, and oblique (projectile) upward throw.
2.A body falls from a height of 60 m. At the same time, another body is launched vertically upward from the ground with initial speed v0 = 120 m.s-1. After what time and at what height above the ground will the two bodies meet?
Solution:
Analysis:
h = 60 m, v0 = 120 m.s-1
h1 + h2 = h
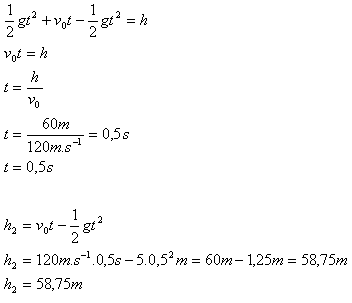
The bodies will meet after 0.5 s at a height of 58.75 m above the ground.
3.A freely falling stone has an instantaneous speed of 50 m.s-1 at one point of its path and, at another lower point, a speed of 80 m.s-1. How long does it take for the stone to fall from the first point to the second, and how far apart are the two points?
Solution:
Analysis:
v1 = 50 m.s-1, v2 = 80 m.s-1
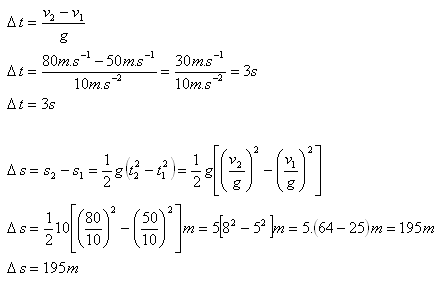
The stone falls from the first to the second point in 3 s. The distance between the points is 195 m.
4. With what speed does the water jet emerge from the fountain nozzle if the water reaches a height of 20 m?
Solution:
Analysis:
h = 20 m, v = ?
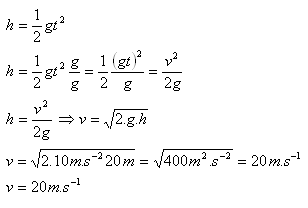
The water jets from the fountain at a speed v = 20 m.s-1.
5. A ball thrown vertically upward returned to the point of release after 2 s. To what height did it rise?
Solution:
Analysis:
2t = 2 s
t = 1 s — the ascent time of the ball
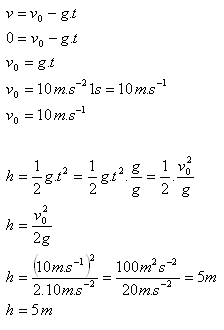
The ball rose to a height of 5 m.
6.From the window of a high-rise building, a boy threw a tennis ball horizontally; it landed after 3 seconds at a distance of 15 m from the building. Determine the height of the window above the ground and the initial speed of the ball.
Solution:
Analysis:
d = 15 m, t = 3 s
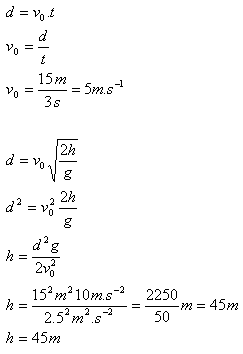
The initial speed of the ball is 5 m.s-1. The height of the window above the ground is 45 m.
7. An airplane drops a bomb on a ship. The plane flies at a height of 320 m above the sea at a speed of 180 km.h-1. The ship moves at a speed of 36 km.h-1. At what distance from the ship must the crew release the bomb so that it hits the ship, if the plane moves
- a) in the same direction as the ship
- b) in the opposite direction to the ship
Solution:
Analysis:
v1 = 180 km.h-1 = 50 m.s-1, v2 = 36 km.h-1 = 10 m.s-1, h = 320 m
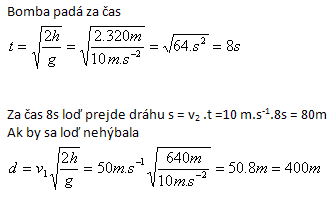
- a) The plane flies in the same direction as the ship: x = d – s = 400 m − 80 m = 320 m in front of the ship
- b) The plane flies in the opposite direction to the ship: y = d + s = 400 m + 80 m = 480 m in front of the ship
8.A shot-putter threw the shot obliquely upward with an initial speed of 10 m.s-1. Compare the range for elevation angles 30o, 45o, 60o.
Solution:
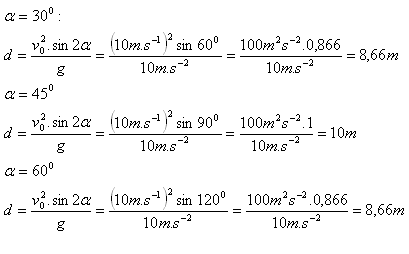
The distances are only theoretical, neglecting air resistance.
9.A body was thrown obliquely upward with an initial speed v0 = 30 m.s-1 at an elevation angle of 50o.
- a) Determine its position at time t = 1.5 s.
- b) What maximum height does it reach?
Solution:
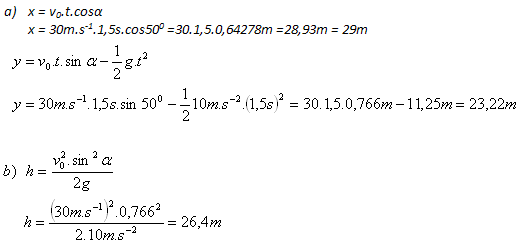
- a) At time t = 1.5 s the body will be at a distance of 29 m from the launch point, at a height of 23.22 m.
- b) At the apex it reaches a maximum height of 26.4 m.
10.A soccer ball was kicked from the field surface at an elevation angle α = 450 and landed on the field surface at a distance of 40 m from the kick point. What was its initial speed and to what maximum height did the ball rise?
Solution:
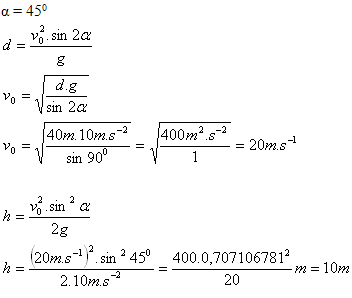
The initial speed of the ball was 20 m.s-1. The ball would rise to a maximum height of 10 m.