State equation
1. What is the relationship between pressure, volume and temperature of an ideal gas?
Solution:
The state of an ideal gas in thermodynamic equilibrium is described by three state variables: pressure p, volume V and thermodynamic temperature T. The mutual relationship between these state variables is expressed by the equation of state for an ideal gas.
The equation of state for an ideal gas:
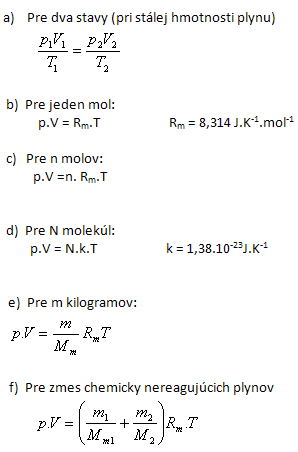
2.Derive the numerical value and the dimension of the molar gas constant Rm.
Solution:
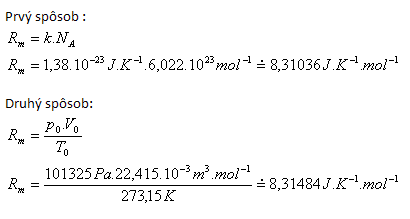
Tabulated value Rm = 3.31441 J·K-1·mol-1.
Differences are caused by different rounding of input values.
3.Find how many molecules are contained in 1 cm3 of any gas under normal conditions.
Solution:
Analysis:
V = 1 cm3 = 10-6 m3, p = 101325 Pa, T = 273.15 K
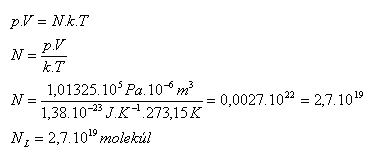
One cubic centimeter of any gas under standard conditions contains NL = 2.7·1019 molecules. This is Loschmidt's number. (Johann Josef Loschmidt 1821–1895)
4. In a vessel with internal volume 8.3 m3 there is hydrogen H2 with mass 200 g and temperature 27oC. Determine its pressure!
Solution:
Analysis:
V = 8.3 m3, m = 200 g = 0.2 kg, t = 27oC, T = (27 + 273.15) K = 300.15 K
Mm = 2·10-3 kg·mol-1, Rm = 8.314 J·K-1·mol-1
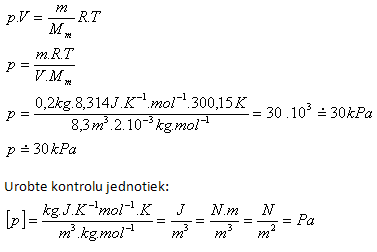
The pressure of hydrogen in the vessel is approximately 30 kPa.
5.In a vessel with internal volume 5·10-3 m3 there is nitrogen N2 at temperature 39oC and pressure 1.6·105 Pa. Determine its mass.
Solution:
Analysis:
V = 5·10-3 m3, p = 1.6·105 Pa, T = 312.15 K, Rm = 8.314 J·K-1·mol-1
Mm = 2.14·10-3 kg·mol-1
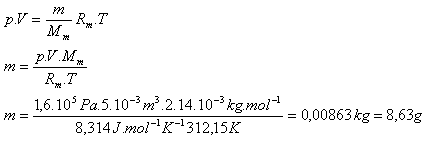
The mass of nitrogen is m = 8.63 g.
6.What is the pressure of air in a truck tire at temperature 20oC and density 8 kg·m-3. Mm(air) = 29·10-3 kg·mol-1
Solution:
Analysis:
T = 293.15 K, ρ = 8 kg·m-3, Mm(air) = 29·10-3 kg·mol-1
Rm = 8.314 J·K-1·mol-1
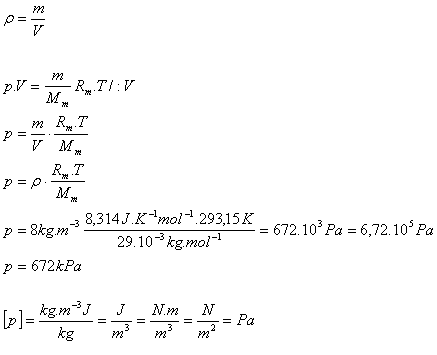
The pressure of the air in the tire is p = 672 kPa.
7.How many molecules are in a spherical vessel of internal radius 3 cm, filled with oxygen O2 at temperature 27oC and pressure 1.36·10-2 Pa.
Solution:
Analysis:
r = 3 cm = 3·10-2 m, T = 300.15 K, p = 1.36·10-2 Pa
k = 1.38·10-23 J·K-1, V = 4/3·π·r3, N = ?
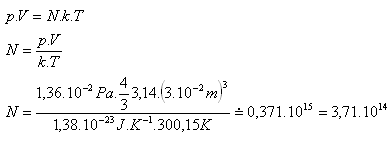
There are N = 3.71·1014 oxygen O2 molecules in the vessel.
8.In a vessel there is nitrogen N2 with mass 10 kg at pressure 10 MPa. Determine the mass of nitrogen that must be released from the vessel so that its pressure decreases to 2.5 MPa. (The temperature of the nitrogen does not change)
Solution:
Analysis:
m1 = 10 kg, p1 = 107 Pa, p2 = 2.5·106 Pa, T = constant
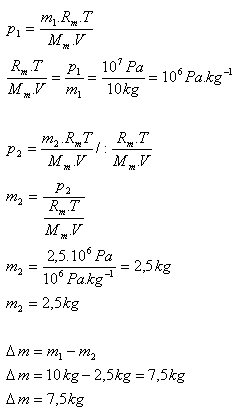
It is necessary to release 7.5 kg of nitrogen from the vessel.
9.The density of nitrogen under standard conditions (T1 = 273.15 K and p1 = 101325 Pa) is ρ1 = 1.23 kg·m-3. Determine the density of nitrogen at temperature 30oC and normal pressure.
Solution:
Analysis:
T1 = 273.15 K, T2 = 303.15 K, p1 = p2 = 101325 Pa, ρ1 = 1.23 kg·m-3, ρ2 = ?
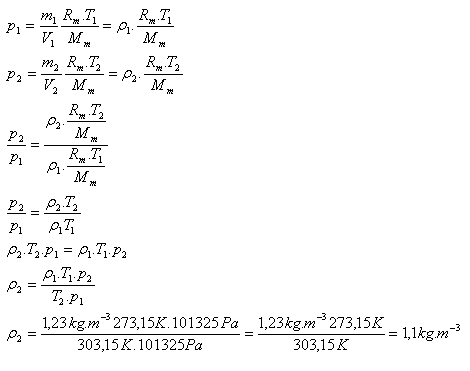
The density of nitrogen at 30oC and normal pressure is 1.1 kg·m-3.
10. Calculate the effective molar mass of air Mm. Consider air as a mixture of 75% nitrogen and 25% oxygen.
Solution:
Analysis:
Mm(N2) = 28·10-3 kg·mol-1, m1(N2) = 0.75 m
Mm(O2) = 32·10-3 kg·mol-1, m2(O2) = 0.25 m
m = total mass of air
Effective molar mass (valid for two chemically non-reacting gases)
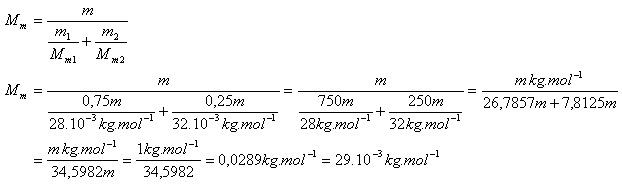
The effective molar mass of air is Mm = 29·10-3 kg·mol-1.