Special theory of relativity
1. Explain the difference between classical physics and the special theory of relativity,
Solution:
Classical physics (Archimedes, Newton) studies the physical properties of bodies that are relatively large and move at low speeds (v << c). It considers mass, length, time, simultaneity of two events, momentum, and energy as constant, independent of the speed of motion.
The special theory of relativity (Einstein) studies the motion of bodies that move at speeds comparable to the speed of light in a vacuum c.
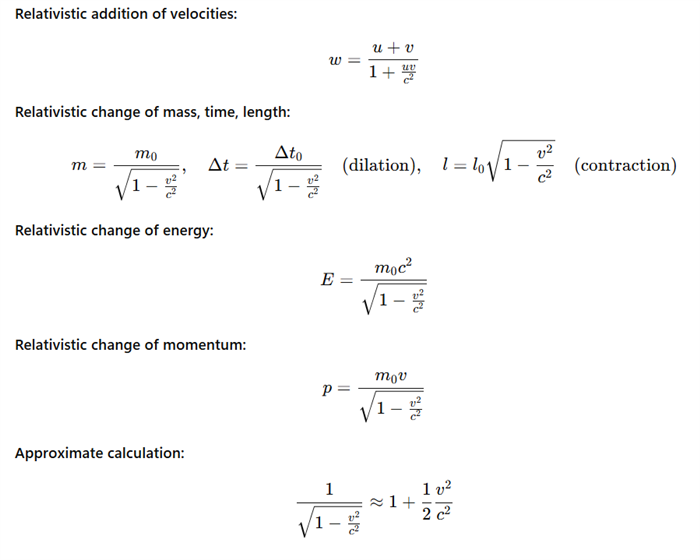
2. From an electron source, two electrons fly out in opposite directions. Each electron has a speed v1 = v2 = 0.8c relative to this gun. What is their relative speed?
Solution:
Analysis:
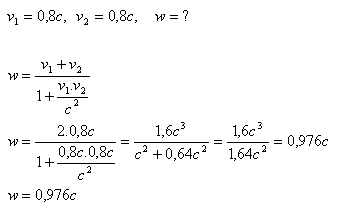
The relative speed of the electrons is w = 0.976c.
3. An α particle flew out of a laboratory accelerator with speed v and moved uniformly in a straight line. It passed through a tube of length 12 cm in 10 ns. What is the length of the tube in the reference frame attached to the α particle?
Solution:
Analysis:
s = 12 cm = 0.12 m, t = 10 ns = 10-9s, l = ?
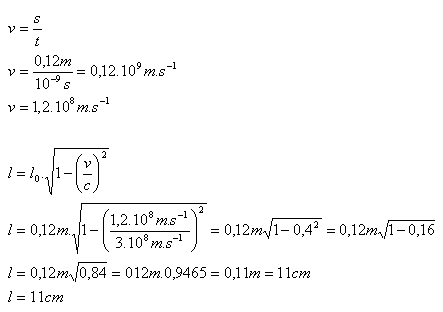
The length of the accelerator tube contracted to 11 cm.
4. A beam of π mesons flies out of an accelerator at speed v = 0.8c. The half-life of π mesons is t0 = 1.8·10-8s. Calculate the time it takes for half of the mesons to decay and the distance they travel before decaying.
Solution:
Analysis:
v = 0.8c, t0 = 1.8·10-8s, t = ?, s = ?
Half of the mesons decay after t = 3·10–8s. During this time they travel a distance s = 7.2 m.
5. The density of iron is ρ0 = 7400 kg·m-3 in the rest frame. How does the density of an iron body change if its speed increases from zero to v = 0.5c?
Solution:
Analysis:
ρ0 = 7400 kg·m-3, v = 0.5c, ρ = ?
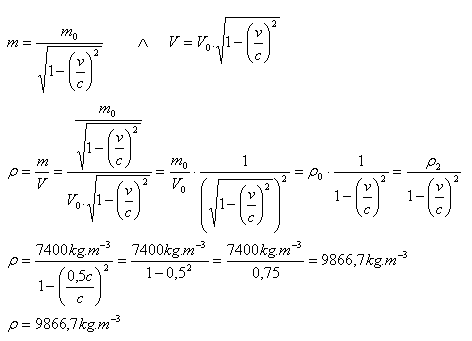
The density of the body changes to ρ = 9866.7 kg·m-3.
6. Calculate the speed at which the relativistic momentum of an α particle is twice as large as the momentum calculated according to the rules of classical mechanics.
Solution:
Analysis:
2p0 = p
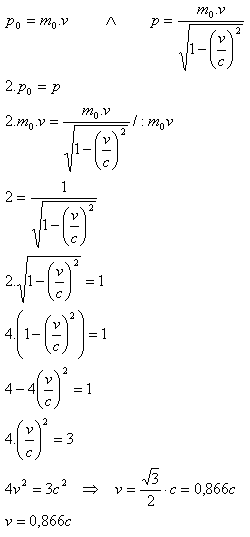
The speed of the α particle is v = 0.866c
7. A spaceship moves relative to Earth at a speed of 12,000 km·s-1. How long does an event that lasts 1 hour on Earth take for an observer in the spaceship?
Solution:
Analysis:
v = 12,000 km·s-1 = 1.2·107 m·s-1, t0 = 1 hour, t = ?
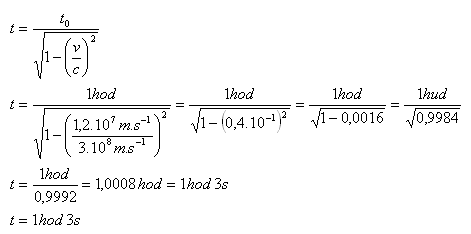
For the observer in the spaceship, the event lasts about 1 hour and 3 seconds.
8. What is the wavelength of a photon whose energy equals the energy of an electron moving at v = 0.6c?
Solution:
Analysis:
v = 0.6c, c = 3·108 m·s-1, h = 6.625·10-34 J·s, me = 9.1·10-31 kg, λ = ?,
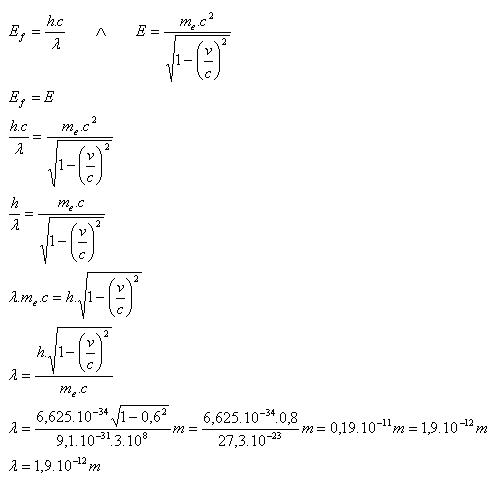
The wavelength of the photon is λ = 1.9·10-12 m.